Let's Encrypt SSL Certificates for Java Developers
Table of Contents
- Overview
- What is Certificate Authority
- Trust Store
- Trust Inheritance
- Certificate Issuance
- Automated Certificate Issuance
- ATSD Integration
- Public Certificate Logging
- Custom CA
- Custom CA Examples
- Miscellaneous
Overview
Let's Encrypt is a non-profit certificate authority established in 2016. It allows web administrators to easily obtain and renew free SSL certificates based on domain validation.
The certificate signing and issuance process is automated based on ACME protocol using Linux packages and plugins for popular web servers.
What is Certificate Authority
CA is a trusted organization authorized to issue public key certificates to end entities (organization, person, domain, program).
Trust is established when the person installs software (OS, browser, Java Runtime/Development Environment, python) containing a list of trusted CAs.
CAs issue certificates which is a file, typically in X509 format, containing information about the issuer (CA), the subject or end entity, the certificate validity dates, issuer signature, and the public key of the subject.
In cases of HTTPS connection, the certificate is presented by the web server (nginx, apache, tomcat, jetty) to the client (browser, curl, apache HTTP client, java URL connection) as part of an SSL handshake.
*.axibase.com old wildcard certificate:
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
13:81:71:6d:80:d8:c8:f1:d4:5f:66:4f:6f:21:6f:6d
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: (CA ID: 1455)
commonName = COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA
organizationName = COMODO CA Limited
localityName = Salford
stateOrProvinceName = Greater Manchester
countryName = GB
Validity
Not Before: Mar 17 00:00:00 2015 GMT
Not After : Mar 16 23:59:59 2018 GMT
Subject:
commonName = *.axibase.com
organizationalUnitName = PositiveSSL Wildcard
organizationalUnitName = Domain Control Validated
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Public-Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
00:cc:e9:99:88:9f:92:25:f5:9e:35:b1:d3:07:43:
....
2a:91
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:90:AF:6A:3A:94:5A:0B:D8:90:EA:12:56:73:DF:43:B4:3A:28:DA:E7
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
85:F2:49:06:2C:14:61:A0:C6:67:8E:75:00:4B:07:30:10:6D:59:11
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:FALSE
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
TLS Web Server Authentication, TLS Web Client Authentication
X509v3 Certificate Policies:
Policy: 1.3.6.1.4.1.6449.1.2.2.7
CPS: https://secure.comodo.com/CPS
Policy: 2.23.140.1.2.1
X509v3 CRL Distribution Points:
Full Name:
URI:http://crl.comodoca.com/COMODORSADomainValidationSecureServerCA.crl
Authority Information Access:
CA Issuers - URI:http://crt.comodoca.com/COMODORSADomainValidationSecureServerCA.crt
OCSP - URI:http://ocsp.comodoca.com
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.axibase.com
DNS:axibase.com
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
8a:d9:06:0e:42:68:48:e7:ab:ec:8f:d9:be:ff:c5:9f:5a:86:
...
The certificate is presented to the client as part of the secure connection negotiations process.
curl SSL handshake:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0* Connected to axibase.com (.....) port 443 (#0)
* Cipher selection: ALL:!EXPORT:!EXPORT40:!EXPORT56:!aNULL:!LOW:!RC4:@STRENGTH
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
CApath: none
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
} [290 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
{ [85 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
{ [2472 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12):
{ [413 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server finished (14):
{ [4 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16):
} [150 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
} [1 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
} [16 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
{ [1 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
{ [16 bytes data]
* SSL connection using TLSv1.2 / ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
* Server certificate:
* subject: CN=*.axibase.com
* start date: Mar 17 00:00:00 2015 GMT
* expire date: Mar 16 23:59:59 2018 GMT
* issuer: C=US; O=Let's Encrypt; CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3
* SSL certificate verify ok.
The client uses its private trust store (CAfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt above) containing the list of trusted CA certificates. These trusted CA certificates are often called Root certificates.
The CA can delegate certificate issuance to other intermediate CAs.
Both the Root CA and any of its intermediate CAs can issue a certificate to any subject.
Trust is established when the issuer of the certificate is present in the client trust store. Trust is also established when the issuer is an intermediate CA whose authority can be verified with a chain of certificates leading to a trusted CA certificate present in the client trust store.
The certificates for intermediate CAs are bundled by web server into an ordered chain which is presented to the client during SSL handshake for verification.
In case of the old *.axibase.com wildcard certificate, the chain is established as follows:
*.axibase.com
issued by COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA
issued by COMODO RSA Certification Authority
issued by AddTrust External CA Root [ROOT]
Let's Encrypt CA Certificates
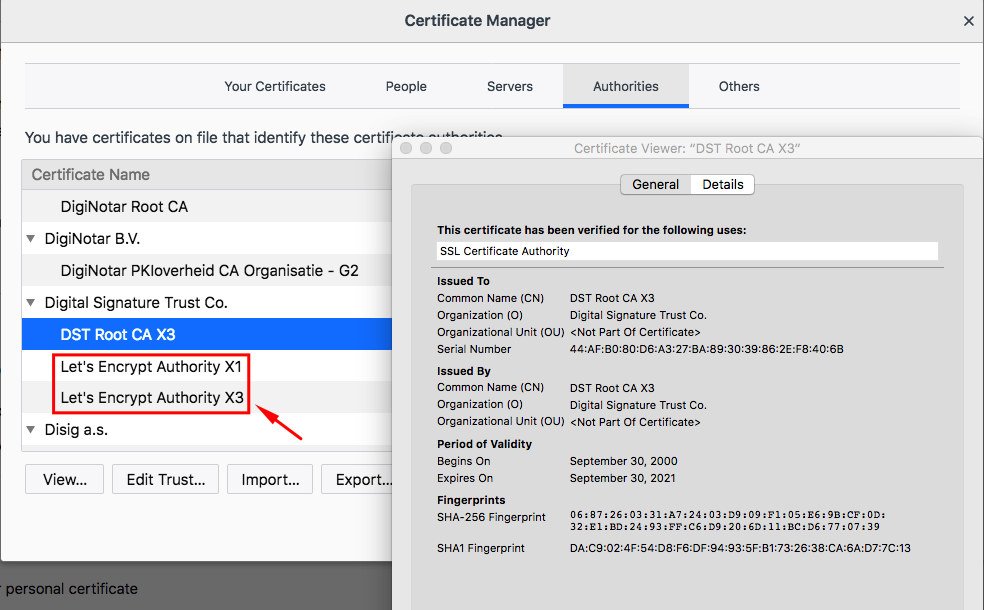
The Let's Encrypt root CA, ISRG Root X1, is not yet present in trust stores.
Let's Encrypt has four intermediate CAs, two of which are signed by other more established CAs who are present in trust stores.
Currently active intermediate CAs:
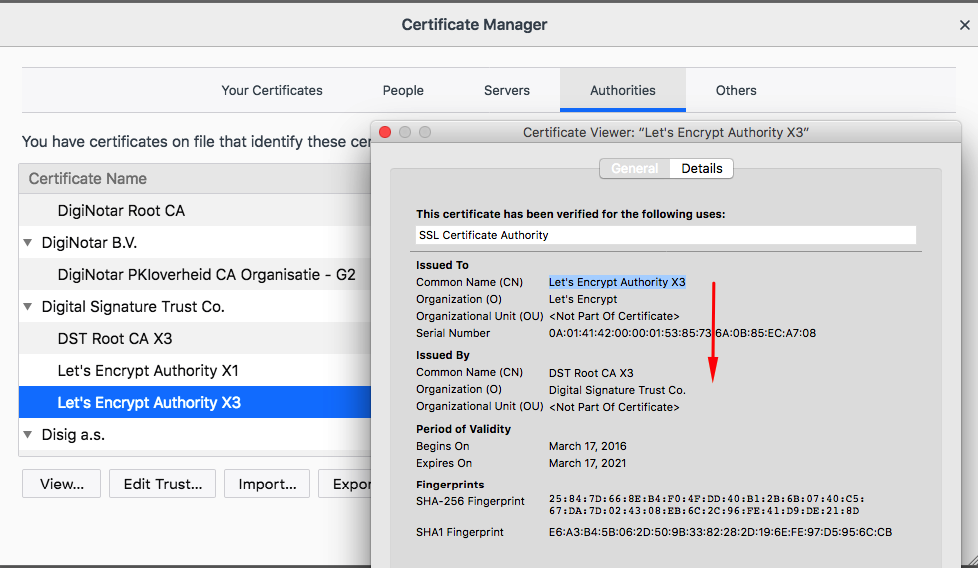
- Let's Encrypt Authority X3
- Let's Encrypt Authority X4
The root CA for X3 and X4 is DST Root CA X3 by Digital Signature Trust Co.. These intermediate certificates expire in less than 3 years.
Sample certificate chain for Let's Encrypt Authority X3-signed certificate:
=== BEGIN chain ===
Subject = CN=nur.axibase.com
Issuer = CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3, O=Let's Encrypt, C=US
Valid = 2018-03-17 - 2018-06-15
:::
Subject = CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3, O=Let's Encrypt, C=US
Issuer = CN=DST Root CA X3, O=Digital Signature Trust Co.
Valid = 2016-03-17 - 2021-03-17
=== END chain ===
Trust Store
Trust store is where a client maintains a list of trusted CAs.
Trust store typically uses JKS (Java specific) or PKCS12 format.
Operating System Trust Store
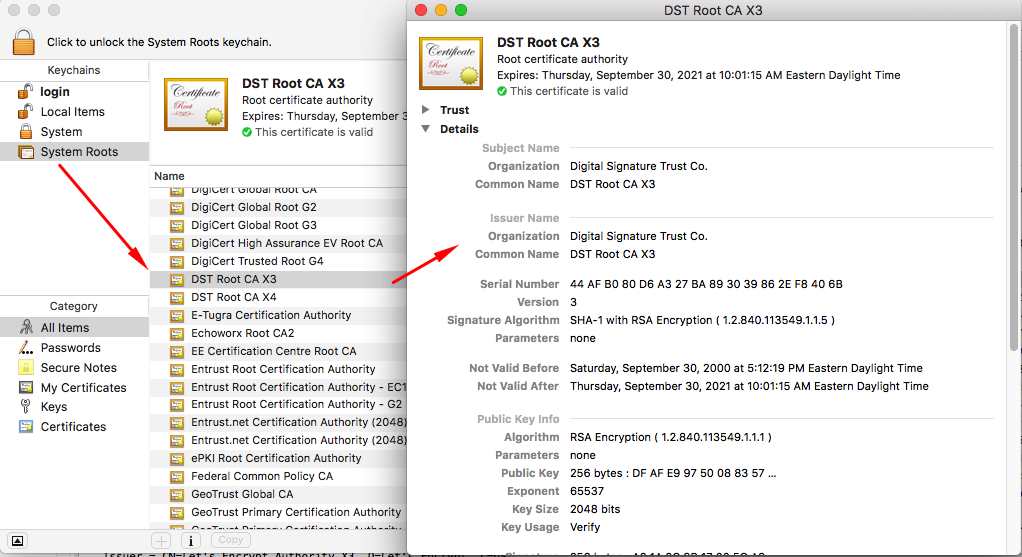
List of Root CAs in MacOS
The list is managed by Apple (company) and is updated with OS patches.
Open Utilities > KeyChain.
List of Root CAs in Ubuntu
The root CA certificates are stored in the /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt directory.
awk -v cmd='openssl x509 -noout -subject' '
/BEGIN/{close(cmd)};{print | cmd}' < /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
The list has 148 entries including the 'DST Root CA X3' certificate.
...
subject= /C=US/O=Digital Signature Trust/OU=DST ACES/CN=DST ACES CA X6
subject= /O=Digital Signature Trust Co./CN=DST Root CA X3
ls /usr/share/ca-certificates/mozilla/
View Ubuntu 14.04 CAs
ACCVRAIZ1.crt Global_Chambersign_Root_-_2008.crt
ACEDICOM_Root.crt GlobalSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_R4.crt
AC_RAIZ_FNMT-RCM.crt GlobalSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_R5.crt
Actalis_Authentication_Root_CA.crt GlobalSign_Root_CA.crt
AddTrust_External_Root.crt GlobalSign_Root_CA_-_R2.crt
AddTrust_Low-Value_Services_Root.crt GlobalSign_Root_CA_-_R3.crt
AddTrust_Public_Services_Root.crt Go_Daddy_Class_2_CA.crt
AddTrust_Qualified_Certificates_Root.crt Go_Daddy_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.crt
AffirmTrust_Commercial.crt Hellenic_Academic_and_Research_Institutions_ECC_RootCA_2015.crt
AffirmTrust_Networking.crt Hellenic_Academic_and_Research_Institutions_RootCA_2011.crt
AffirmTrust_Premium.crt Hellenic_Academic_and_Research_Institutions_RootCA_2015.crt
AffirmTrust_Premium_ECC.crt Hongkong_Post_Root_CA_1.crt
Amazon_Root_CA_1.crt IdenTrust_Commercial_Root_CA_1.crt
Amazon_Root_CA_2.crt IdenTrust_Public_Sector_Root_CA_1.crt
Amazon_Root_CA_3.crt ISRG_Root_X1.crt
Amazon_Root_CA_4.crt Izenpe.com.crt
Atos_TrustedRoot_2011.crt LuxTrust_Global_Root_2.crt
Autoridad_de_Certificacion_Firmaprofesional_CIF_A62634068.crt Microsec_e-Szigno_Root_CA_2009.crt
Baltimore_CyberTrust_Root.crt NetLock_Arany_=Class_Gold=_Főtanúsítvány.crt
Buypass_Class_2_Root_CA.crt Network_Solutions_Certificate_Authority.crt
Buypass_Class_3_Root_CA.crt OISTE_WISeKey_Global_Root_GA_CA.crt
CA_Disig_Root_R1.crt OISTE_WISeKey_Global_Root_GB_CA.crt
CA_Disig_Root_R2.crt OpenTrust_Root_CA_G1.crt
Camerfirma_Chambers_of_Commerce_Root.crt OpenTrust_Root_CA_G2.crt
Camerfirma_Global_Chambersign_Root.crt OpenTrust_Root_CA_G3.crt
Certigna.crt PSCProcert.crt
Certinomis_-_Autorité_Racine.crt QuoVadis_Root_CA_1_G3.crt
Certinomis_-_Root_CA.crt QuoVadis_Root_CA_2.crt
Certplus_Class_2_Primary_CA.crt QuoVadis_Root_CA_2_G3.crt
Certplus_Root_CA_G1.crt QuoVadis_Root_CA_3.crt
Certplus_Root_CA_G2.crt QuoVadis_Root_CA_3_G3.crt
certSIGN_ROOT_CA.crt QuoVadis_Root_CA.crt
Certum_Root_CA.crt Secure_Global_CA.crt
Certum_Trusted_Network_CA_2.crt SecureSign_RootCA11.crt
Certum_Trusted_Network_CA.crt SecureTrust_CA.crt
CFCA_EV_ROOT.crt Security_Communication_EV_RootCA1.crt
Chambers_of_Commerce_Root_-_2008.crt Security_Communication_RootCA2.crt
China_Internet_Network_Information_Center_EV_Certificates_Root.crt Security_Communication_Root_CA.crt
CNNIC_ROOT.crt Sonera_Class_2_Root_CA.crt
Comodo_AAA_Services_root.crt Staat_der_Nederlanden_EV_Root_CA.crt
COMODO_Certification_Authority.crt Staat_der_Nederlanden_Root_CA_-_G2.crt
COMODO_ECC_Certification_Authority.crt Staat_der_Nederlanden_Root_CA_-_G3.crt
COMODO_RSA_Certification_Authority.crt Starfield_Class_2_CA.crt
Comodo_Secure_Services_root.crt Starfield_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.crt
Comodo_Trusted_Services_root.crt Starfield_Services_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.crt
Cybertrust_Global_Root.crt Swisscom_Root_CA_1.crt
Deutsche_Telekom_Root_CA_2.crt Swisscom_Root_CA_2.crt
DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_CA.crt Swisscom_Root_EV_CA_2.crt
DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_G2.crt SwissSign_Gold_CA_-_G2.crt
DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_G3.crt SwissSign_Silver_CA_-_G2.crt
DigiCert_Global_Root_CA.crt SZAFIR_ROOT_CA2.crt
DigiCert_Global_Root_G2.crt Taiwan_GRCA.crt
DigiCert_Global_Root_G3.crt TeliaSonera_Root_CA_v1.crt
DigiCert_High_Assurance_EV_Root_CA.crt thawte_Primary_Root_CA.crt
DigiCert_Trusted_Root_G4.crt thawte_Primary_Root_CA_-_G2.crt
DST_ACES_CA_X6.crt thawte_Primary_Root_CA_-_G3.crt
DST_Root_CA_X3.crt Trustis_FPS_Root_CA.crt
D-TRUST_Root_Class_3_CA_2_2009.crt T-TeleSec_GlobalRoot_Class_2.crt
D-TRUST_Root_Class_3_CA_2_EV_2009.crt T-TeleSec_GlobalRoot_Class_3.crt
EC-ACC.crt TUBITAK_Kamu_SM_SSL_Kok_Sertifikasi_-_Surum_1.crt
EE_Certification_Centre_Root_CA.crt TÜBİTAK_UEKAE_Kök_Sertifika_Hizmet_Sağlayıcısı_-_Sürüm_3.crt
Entrust.net_Premium_2048_Secure_Server_CA.crt TURKTRUST_Certificate_Services_Provider_Root_2007.crt
Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority.crt TÜRKTRUST_Elektronik_Sertifika_Hizmet_Sağlayıcısı_H5.crt
Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_EC1.crt TWCA_Global_Root_CA.crt
Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_G2.crt TWCA_Root_Certification_Authority.crt
ePKI_Root_Certification_Authority.crt USERTrust_ECC_Certification_Authority.crt
E-Tugra_Certification_Authority.crt USERTrust_RSA_Certification_Authority.crt
GeoTrust_Global_CA_2.crt UTN_USERFirst_Hardware_Root_CA.crt
GeoTrust_Global_CA.crt Verisign_Class_3_Public_Primary_Certification_Authority_-_G3.crt
GeoTrust_Primary_Certification_Authority.crt VeriSign_Class_3_Public_Primary_Certification_Authority_-_G4.crt
GeoTrust_Primary_Certification_Authority_-_G2.crt VeriSign_Class_3_Public_Primary_Certification_Authority_-_G5.crt
GeoTrust_Primary_Certification_Authority_-_G3.crt VeriSign_Universal_Root_Certification_Authority.crt
GeoTrust_Universal_CA_2.crt Visa_eCommerce_Root.crt
GeoTrust_Universal_CA.crt XRamp_Global_CA_Root.crt
The list of root CAs is updated through the ca-certificates package.
Search apt package manager history to view when the ca-certificates package is last updated.
zgrep ca-certificates /var/log/apt/history*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3300 Oct 30 09:55 history.log.6.gz
ca-certificates:amd64 (20160104ubuntu0.14.04.1, 20170717~14.04.1)
ca-certificates-java:amd64 (20130815ubuntu1)
The list of changes performed on a specific version of the ca-certificates package is summarized in the package change log:
ca-certificates (20170717) unstable; urgency=medium
* mozilla/{certdata.txt,nssckbi.h}:
The following certificate authorities were added (+):
+ "AC RAIZ FNMT-RCM"
+ "Amazon Root CA 1"
+ "Amazon Root CA 2"
+ "Amazon Root CA 3"
+ "Amazon Root CA 4"
+ "D-TRUST Root CA 3 2013"
+ "LuxTrust Global Root 2"
+ "TUBITAK Kamu SM SSL Kok Sertifikasi - Surum 1"
The following certificate authorities were removed (-):
- "AC Raiz Certicamara S.A."
- "ApplicationCA - Japanese Government"
- "Buypass Class 2 CA 1"
- "ComSign CA"
- "EBG Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Saglayicisi"
- "Equifax Secure CA"
- "Equifax Secure eBusiness CA 1"
- "Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA"
- "IGC/A"
- "Juur-SK"
- "Microsec e-Szigno Root CA"
- "Root CA Generalitat Valenciana"
- "RSA Security 2048 v3"
- "S-TRUST Authentication and Encryption Root CA 2005 PN"
- "S-TRUST Universal Root CA"
- "SwissSign Platinum CA - G2"
- "TC TrustCenter Class 3 CA II"
- "TÜRKTRUST Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı H6"
- "UTN USERFirst Email Root CA"
- "Verisign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority"
- "Verisign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3"
- "Verisign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2"
- "Verisign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3"
- "Verisign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority"
- "WellsSecure Public Root Certificate Authority"
Browser Trust Store
- Chrome defers to the list of Root CAs maintained by the operating system.
- Mozilla Firefox maintains its own list of Root CAs.
The changes are subject to review. It takes 2 years to become a Mozilla root CA.
The updated list is propagated to users via browser patches.
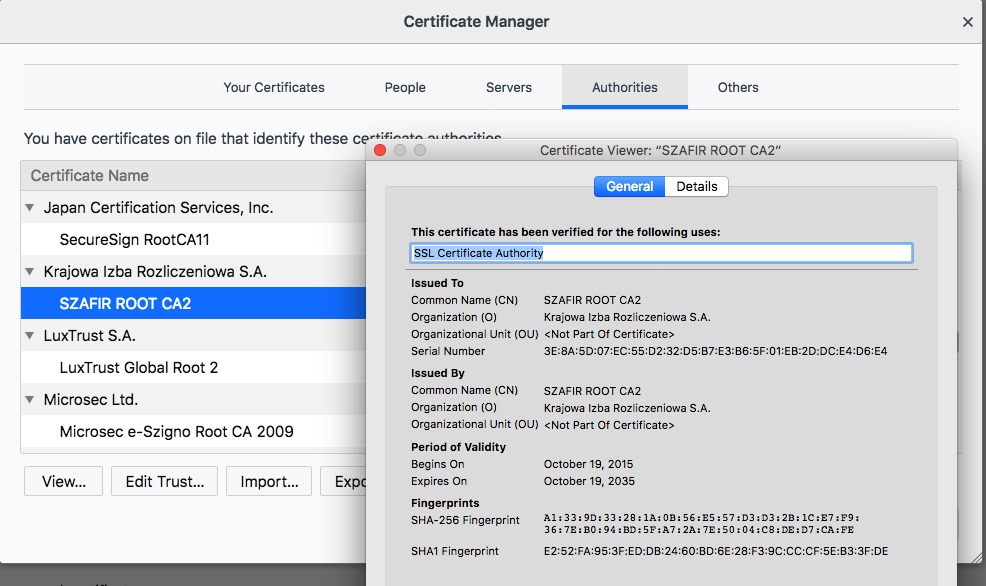
Application Trust Store
Applications can elect to utilize their own, built-in, trust store or utilize the trust store of the underlying operating system.
- Python
The Requests module uses certificates from the certifi package.
Certifi is a carefully curated collection of Root Certificates for validating the trustworthiness of SSL certificates while verifying the identity of TLS hosts. It has been extracted from the Requests project. Certifi updates its list based on Mozilla certdata.txt.
- Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
import java.security.KeyStore;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import javax.naming.ldap.LdapName;
public class CertListCA {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String trustPath = System.getProperties().get("java.home") + "/lib/security/cacerts";
System.out.println(" trust.path= " + trustPath);
KeyStore trustStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
trustStore.load(new FileInputStream(trustPath), "changeit".toCharArray());
Collections.list(trustStore.aliases()).stream().sorted(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER).forEach(
rootAlias -> {
try {
X509Certificate caCert = (X509Certificate)trustStore.getCertificate(rootAlias);
LdapName issuerName = new LdapName(caCert.getIssuerDN().getName());
String issuerCN = issuerName.getRdns().stream().filter(rdn -> rdn.getType().equalsIgnoreCase("cn")).map(rdn -> rdn.getValue().toString()).collect(Collectors.joining( "," ));
if (issuerCN.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(" no CN = " + caCert.getIssuerDN().getName());
} else {
System.out.println(" CN = " + issuerCN);
}
} catch (Exception ke) {
ke.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
View OpenJDK 1.8.0_162 CAs
trust.path= /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/lib/security/cacerts
CN = AC Raíz Certicámara S.A.
CN = ACCVRAIZ1
CN = ACEDICOM Root
CN = Actalis Authentication Root CA
CN = AddTrust External CA Root
CN = AddTrust Class 1 CA Root
CN = AddTrust Public CA Root
CN = AddTrust Qualified CA Root
CN = AffirmTrust Commercial
CN = AffirmTrust Networking
CN = AffirmTrust Premium
CN = AffirmTrust Premium ECC
no CN = OU=ApplicationCA, O=Japanese Government, C=JP
CN = Atos TrustedRoot 2011
CN = Autoridad de Certificacion Firmaprofesional CIF A62634068
CN = Baltimore CyberTrust Root
CN = Buypass Class 2 CA 1
CN = Buypass Class 2 Root CA
CN = Buypass Class 3 Root CA
CN = CA Disig Root R1
CN = CA Disig Root R2
CN = Chambers of Commerce Root
CN = Global Chambersign Root
CN = Certigna
CN = Certinomis - Autorité Racine
CN = Certinomis - Root CA
CN = Class 2 Primary CA
CN = Certplus Root CA G1
CN = Certplus Root CA G2
no CN = OU=certSIGN ROOT CA, O=certSIGN, C=RO
CN = Certum CA
CN = Certum Trusted Network CA
CN = Certum Trusted Network CA 2
CN = CFCA EV ROOT
CN = Chambers of Commerce Root - 2008
CN = China Internet Network Information Center EV Certificates Root
CN = CNNIC ROOT
CN = AAA Certificate Services
CN = COMODO Certification Authority
CN = COMODO ECC Certification Authority
CN = COMODO RSA Certification Authority
CN = Secure Certificate Services
CN = Trusted Certificate Services
CN = ComSign CA
CN = Cybertrust Global Root
CN = D-TRUST Root Class 3 CA 2 2009
CN = D-TRUST Root Class 3 CA 2 EV 2009
CN = Deutsche Telekom Root CA 2
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root CA
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root G2
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root G3
CN = DigiCert Global Root CA
CN = DigiCert Global Root G2
CN = DigiCert Global Root G3
CN = DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA
CN = DigiCert Trusted Root G4
CN = DST ACES CA X6
CN = DST Root CA X3
CN = E-Tugra Certification Authority
CN = EBG Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı
CN = EC-ACC
CN = EE Certification Centre Root CA
CN = Entrust.net Certification Authority (2048)
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority - EC1
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2
no CN = OU=ePKI Root Certification Authority, O="Chunghwa Telecom Co., Ltd.", C=TW
no CN = OU=Equifax Secure Certificate Authority, O=Equifax, C=US
CN = Equifax Secure eBusiness CA-1
CN = Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA-1
CN = GeoTrust Global CA
CN = GeoTrust Global CA 2
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G2
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G3
CN = GeoTrust Universal CA
CN = GeoTrust Universal CA 2
CN = Global Chambersign Root - 2008
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign Root CA
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign
no CN = OU=Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority, O="The Go Daddy Group, Inc.", C=US
CN = Go Daddy Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Hellenic Academic and Research Institutions ECC RootCA 2015
CN = Hellenic Academic and Research Institutions RootCA 2011
CN = Hellenic Academic and Research Institutions RootCA 2015
CN = Hongkong Post Root CA 1
CN = IdenTrust Commercial Root CA 1
CN = IdenTrust Public Sector Root CA 1
CN = IGC/A
CN = ISRG Root X1
CN = Izenpe.com
CN = Juur-SK
CN = Microsec e-Szigno Root CA
CN = Microsec e-Szigno Root CA 2009
CN = NetLock Arany (Class Gold) Főtanúsítvány
CN = Network Solutions Certificate Authority
CN = OISTE WISeKey Global Root GA CA
CN = OISTE WISeKey Global Root GB CA
CN = OpenTrust Root CA G1
CN = OpenTrust Root CA G2
CN = OpenTrust Root CA G3
CN = Autoridad de Certificacion Raiz del Estado Venezolano
CN = QuoVadis Root Certification Authority
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 1 G3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 2
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 2 G3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 3 G3
CN = Root CA Generalitat Valenciana
no CN = OU=RSA Security 2048 V3, O=RSA Security Inc
CN = S-TRUST Authentication and Encryption Root CA 2005:PN
CN = S-TRUST Universal Root CA
CN = Secure Global CA
CN = SecureSign RootCA11
CN = SecureTrust CA
no CN = OU=Security Communication EV RootCA1, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP
no CN = OU=Security Communication RootCA1, O=SECOM Trust.net, C=JP
no CN = OU=Security Communication RootCA2, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP
CN = Sonera Class2 CA
CN = Staat der Nederlanden EV Root CA
CN = Staat der Nederlanden Root CA - G2
CN = Staat der Nederlanden Root CA - G3
no CN = OU=Starfield Class 2 Certification Authority, O="Starfield Technologies, Inc.", C=US
CN = Starfield Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Starfield Services Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Swisscom Root CA 1
CN = Swisscom Root CA 2
CN = Swisscom Root EV CA 2
CN = SwissSign Gold CA - G2
CN = SwissSign Platinum CA - G2
CN = SwissSign Silver CA - G2
CN = SZAFIR ROOT CA2
CN = T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 2
CN = T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 3
no CN = O=Government Root Certification Authority, C=TW
CN = TC TrustCenter Class 3 CA II
CN = TeliaSonera Root CA v1
CN = thawte Primary Root CA
CN = thawte Primary Root CA - G2
CN = thawte Primary Root CA - G3
no CN = OU=Trustis FPS Root CA, O=Trustis Limited, C=GB
CN = TÜRKTRUST Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı
CN = TWCA Global Root CA
CN = TWCA Root Certification Authority
CN = TÜBİTAK UEKAE Kök Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı - Sürüm 3
CN = TÜRKTRUST Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı H5
CN = TÜRKTRUST Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı H6
CN = USERTrust ECC Certification Authority
CN = USERTrust RSA Certification Authority
CN = UTN-USERFirst-Client Authentication and Email
CN = UTN-USERFirst-Hardware
no CN = OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
no CN = OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
no CN = OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G4
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5
CN = VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority
CN = Visa eCommerce Root
CN = WellsSecure Public Root Certificate Authority
CN = XRamp Global Certification Authority
OpenJDK 9
Until fix JEP 319, the OpenJDK 9 binary for Linux x64 contains an empty cacerts keystore.
View OpenJDK 9 CAs
trust.path= /usr/lib/jvm/java-9-openjdk-amd64/lib/security/cacerts
no CN = OU=AC RAIZ FNMT-RCM, O=FNMT-RCM, C=ES
CN = ACCVRAIZ1
CN = ACEDICOM Root
CN = Actalis Authentication Root CA
CN = AddTrust External CA Root
CN = AddTrust Class 1 CA Root
CN = AddTrust Public CA Root
CN = AddTrust Qualified CA Root
CN = AffirmTrust Commercial
CN = AffirmTrust Networking
CN = AffirmTrust Premium
CN = AffirmTrust Premium ECC
CN = Amazon Root CA 1
CN = Amazon Root CA 2
CN = Amazon Root CA 3
CN = Amazon Root CA 4
CN = Atos TrustedRoot 2011
CN = Autoridad de Certificacion Firmaprofesional CIF A62634068
CN = Baltimore CyberTrust Root
CN = Buypass Class 2 Root CA
CN = Buypass Class 3 Root CA
CN = CA Disig Root R1
CN = CA Disig Root R2
CN = Chambers of Commerce Root
CN = Global Chambersign Root
CN = Certigna
CN = Certinomis - Autorité Racine
CN = Certinomis - Root CA
CN = Class 2 Primary CA
CN = Certplus Root CA G1
CN = Certplus Root CA G2
no CN = OU=certSIGN ROOT CA, O=certSIGN, C=RO
CN = Certum CA
CN = Certum Trusted Network CA
CN = Certum Trusted Network CA 2
CN = CFCA EV ROOT
CN = Chambers of Commerce Root - 2008
CN = China Internet Network Information Center EV Certificates Root
CN = CNNIC ROOT
CN = AAA Certificate Services
CN = COMODO Certification Authority
CN = COMODO ECC Certification Authority
CN = COMODO RSA Certification Authority
CN = Secure Certificate Services
CN = Trusted Certificate Services
CN = Cybertrust Global Root
CN = D-TRUST Root Class 3 CA 2 2009
CN = D-TRUST Root Class 3 CA 2 EV 2009
CN = Deutsche Telekom Root CA 2
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root CA
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root G2
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root G3
CN = DigiCert Global Root CA
CN = DigiCert Global Root G2
CN = DigiCert Global Root G3
CN = DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA
CN = DigiCert Trusted Root G4
CN = DST ACES CA X6
CN = DST Root CA X3
CN = E-Tugra Certification Authority
CN = EC-ACC
CN = EE Certification Centre Root CA
CN = Entrust.net Certification Authority (2048)
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority - EC1
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2
no CN = OU=ePKI Root Certification Authority, O="Chunghwa Telecom Co., Ltd.", C=TW
CN = GeoTrust Global CA
CN = GeoTrust Global CA 2
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G2
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G3
CN = GeoTrust Universal CA
CN = GeoTrust Universal CA 2
CN = Global Chambersign Root - 2008
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign Root CA
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign
no CN = OU=Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority, O="The Go Daddy Group, Inc.", C=US
CN = Go Daddy Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Hellenic Academic and Research Institutions ECC RootCA 2015
CN = Hellenic Academic and Research Institutions RootCA 2011
CN = Hellenic Academic and Research Institutions RootCA 2015
CN = Hongkong Post Root CA 1
CN = IdenTrust Commercial Root CA 1
CN = IdenTrust Public Sector Root CA 1
CN = ISRG Root X1
CN = Izenpe.com
CN = LuxTrust Global Root 2
CN = Microsec e-Szigno Root CA 2009
CN = NetLock Arany (Class Gold) Főtanúsítvány
CN = Network Solutions Certificate Authority
CN = OISTE WISeKey Global Root GA CA
CN = OISTE WISeKey Global Root GB CA
CN = OpenTrust Root CA G1
CN = OpenTrust Root CA G2
CN = OpenTrust Root CA G3
CN = Autoridad de Certificacion Raiz del Estado Venezolano
CN = QuoVadis Root Certification Authority
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 1 G3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 2
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 2 G3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 3 G3
CN = Secure Global CA
CN = SecureSign RootCA11
CN = SecureTrust CA
no CN = OU=Security Communication EV RootCA1, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP
no CN = OU=Security Communication RootCA1, O=SECOM Trust.net, C=JP
no CN = OU=Security Communication RootCA2, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP
CN = Sonera Class2 CA
CN = Staat der Nederlanden EV Root CA
CN = Staat der Nederlanden Root CA - G2
CN = Staat der Nederlanden Root CA - G3
no CN = OU=Starfield Class 2 Certification Authority, O="Starfield Technologies, Inc.", C=US
CN = Starfield Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Starfield Services Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Swisscom Root CA 1
CN = Swisscom Root CA 2
CN = Swisscom Root EV CA 2
CN = SwissSign Gold CA - G2
CN = SwissSign Silver CA - G2
CN = SZAFIR ROOT CA2
CN = T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 2
CN = T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 3
no CN = O=Government Root Certification Authority, C=TW
CN = TeliaSonera Root CA v1
CN = thawte Primary Root CA
CN = thawte Primary Root CA - G2
CN = thawte Primary Root CA - G3
no CN = OU=Trustis FPS Root CA, O=Trustis Limited, C=GB
CN = TUBITAK Kamu SM SSL Kok Sertifikasi - Surum 1
CN = TÜRKTRUST Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı
CN = TWCA Global Root CA
CN = TWCA Root Certification Authority
CN = TÜBİTAK UEKAE Kök Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı - Sürüm 3
CN = TÜRKTRUST Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı H5
CN = USERTrust ECC Certification Authority
CN = USERTrust RSA Certification Authority
CN = UTN-USERFirst-Hardware
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G4
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5
CN = VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority
CN = Visa eCommerce Root
CN = XRamp Global Certification Authority
diff --unchanged-line-format="" --old-line-format="" --new-line-format="%L" java8_ca.txt java9_ca.txt
New CAs in OpenJDK 8 -> 9:
no CN = OU=AC RAIZ FNMT-RCM, O=FNMT-RCM, C=ES
CN = Amazon Root CA 1
CN = Amazon Root CA 2
CN = Amazon Root CA 3
CN = Amazon Root CA 4
CN = LuxTrust Global Root 2
CN = TUBITAK Kamu SM SSL Kok Sertifikasi - Surum 1
Removed CAs in OpenJDK 8 -> 9:
CN = AC Raíz Certicámara S.A.
no CN = OU=ApplicationCA, O=Japanese Government, C=JP
CN = Buypass Class 2 CA 1
CN = ComSign CA
CN = EBG Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı
no CN = OU=Equifax Secure Certificate Authority, O=Equifax, C=US
CN = Equifax Secure eBusiness CA-1
CN = Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA-1
CN = IGC/A
CN = Juur-SK
CN = Microsec e-Szigno Root CA
CN = Root CA Generalitat Valenciana
no CN = OU=RSA Security 2048 V3, O=RSA Security Inc
CN = S-TRUST Authentication and Encryption Root CA 2005:PN
CN = S-TRUST Universal Root CA
CN = SwissSign Platinum CA - G2
CN = TC TrustCenter Class 3 CA II
CN = TÜRKTRUST Elektronik Sertifika Hizmet Sağlayıcısı H6
CN = UTN-USERFirst-Client Authentication and Email
no CN = OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
no CN = OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
no CN = OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = WellsSecure Public Root Certificate Authority
View Oracle OpenJDK 1.8.0_131 CAs
trust.path= /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_131.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/security/cacerts
CN = Actalis Authentication Root CA
CN = AddTrust Class 1 CA Root
CN = AddTrust External CA Root
CN = AddTrust Qualified CA Root
CN = AffirmTrust Commercial
CN = AffirmTrust Networking
CN = AffirmTrust Premium
CN = AffirmTrust Premium ECC
CN = America Online Root Certification Authority 1
CN = America Online Root Certification Authority 2
CN = Baltimore CyberTrust Code Signing Root
CN = Baltimore CyberTrust Root
CN = Buypass Class 2 Root CA
CN = Buypass Class 3 Root CA
CN = Chambers of Commerce Root - 2008
CN = Chambers of Commerce Root
CN = Global Chambersign Root - 2008
CN = Class 2 Primary CA
CN = Class 3P Primary CA
CN = Certum CA
CN = Certum Trusted Network CA
no CN = OU=ePKI Root Certification Authority, O="Chunghwa Telecom Co., Ltd.", C=TW
CN = AAA Certificate Services
CN = COMODO ECC Certification Authority
CN = COMODO RSA Certification Authority
CN = Deutsche Telekom Root CA 2
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root G2
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root G3
CN = DigiCert Assured ID Root CA
CN = DigiCert Global Root CA
CN = DigiCert Global Root G2
CN = DigiCert Global Root G3
CN = DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA
CN = DigiCert Trusted Root G4
CN = D-TRUST Root Class 3 CA 2 2009
CN = D-TRUST Root Class 3 CA 2 EV 2009
CN = Entrust.net Certification Authority (2048)
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority - EC1
CN = Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2
no CN = OU=Equifax Secure Certificate Authority, O=Equifax, C=US
CN = Equifax Secure eBusiness CA-1
CN = Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA-1
CN = GeoTrust Global CA
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G2
CN = GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G3
CN = GeoTrust Universal CA
CN = GlobalSign Root CA
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign
CN = GlobalSign
no CN = OU=Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority, O="The Go Daddy Group, Inc.", C=US
CN = Go Daddy Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = GTE CyberTrust Global Root
CN = IdenTrust Commercial Root CA 1
CN = DST Root CA X3
CN = IdenTrust Public Sector Root CA 1
CN = KEYNECTIS ROOT CA
CN = LuxTrust Global Root
CN = QuoVadis Root Certification Authority
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 1 G3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 2
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 2 G3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 3
CN = QuoVadis Root CA 3 G3
no CN = OU=Security Communication EV RootCA1, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP
no CN = OU=Security Communication RootCA1, O=SECOM Trust.net, C=JP
no CN = OU=Security Communication RootCA2, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP
CN = SecureTrust CA
CN = Sonera Class2 CA
no CN = OU=Starfield Class 2 Certification Authority, O="Starfield Technologies, Inc.", C=US
CN = Starfield Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Starfield Services Root Certificate Authority - G2
CN = Swisscom Root CA 2
CN = Swisscom Root EV CA 2
CN = SwissSign Gold CA - G2
CN = SwissSign Platinum CA - G2
CN = SwissSign Silver CA - G2
CN = Thawte Premium Server CA
CN = thawte Primary Root CA
CN = thawte Primary Root CA - G2
CN = thawte Primary Root CA - G3
CN = T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 2
CN = T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 3
CN = USERTrust ECC Certification Authority
CN = USERTrust RSA Certification Authority
CN = UTN-USERFirst-Client Authentication and Email
CN = UTN-USERFirst-Hardware
CN = UTN-USERFirst-Object
no CN = OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
no CN = OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
no CN = OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
no CN = OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
no CN = OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G4
CN = VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5
CN = Thawte Timestamping CA
CN = VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority
CN = XRamp Global Certification Authority
Trust Inheritance
When establishing a secure connection based on X509 certificates, the client is presented not only with the domain certificate of the server, but also with a list of intermediate certificates leading to the root CA in the client trust store.
The list of hierarchically validated certificates is called a certificate chain.
Domain Certificate (1)
Intermediate Certificate (2)
Intermediate Certificate (3)
Root Certificate (4)
The chain of client trust is (4) -> (3) -> (2) -> (1).
- The client trusts Root Certificate (4) because it is in the clients trust store
- The client trusts Intermediate Certificate (3) because it is signed by Root Certificate (4).
- The client trusts Intermediate Certificate (2), because it is signed by Intermediate Certificate (3).
- The client trusts Domain Certificate (1), because it is signed by Intermediate Certificate (2).
The client traverses the chain up until it finds a root CA in its trust store and verifies the validity of the chain using public keys and signatures embedded in each certificate.
Viewing Certificate Chain in Java
import java.io.*;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.cert.*;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.*;
public class CertListChain {
public static final DateTimeFormatter DF = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE.withZone( ZoneId.of("UTC") );
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String path = args[0];
String password = args[1];
String alias = args[2];
KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
// Load certificates from a password-protected file in JKS format
keyStore.load(new FileInputStream(new File(path)), password.toCharArray());
// Retrieve certificates from the keystore for the given alias
Certificate[] certificateChain = keyStore.getCertificateChain(alias);
// Cast certificates to X509Certificate
X509Certificate[] chain = Arrays.stream(certificateChain).toArray(X509Certificate[]::new);
// Print the X509 chain
for (X509Certificate c : chain) {
System.out.println(" Subject = " + c.getSubjectDN().getName());
System.out.println(" Issuer = " + c.getIssuerDN().getName());
System.out.println(" Valid = " + DF.format(c.getNotBefore().toInstant()) + " - " + DF.format(c.getNotAfter().toInstant()));
}
}
}
Self-Signed Certificate Chain
Self-Signed certificates have no chain.
The subject is the same as the issuer.
Subject = CN=atsd, OU=Software Group, O=Axibase Corporation, L=Cupertino, ST=CA, C=US
Issuer = CN=atsd, OU=Software Group, O=Axibase Corporation, L=Cupertino, ST=CA, C=US
Valid = 2017-01-18 - 2017-04-18
CA-Signed Certificate Chain
CA-Signed Certificate.
Subject = CN=*.axibase.com, OU=PositiveSSL Wildcard, OU=Domain Control Validated
Issuer = CN=COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA, O=COMODO CA Limited, L=Salford, ST=Greater Manchester, C=GB
Valid = 2015-03-17 - 2018-03-16
:::
Subject = CN=COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA, O=COMODO CA Limited, L=Salford, ST=Greater Manchester, C=GB
Issuer = CN=COMODO RSA Certification Authority, O=COMODO CA Limited, L=Salford, ST=Greater Manchester, C=GB
Valid = 2014-02-12 - 2029-02-11
:::
Subject = CN=COMODO RSA Certification Authority, O=COMODO CA Limited, L=Salford, ST=Greater Manchester, C=GB
Issuer = CN=AddTrust External CA Root, OU=AddTrust External TTP Network, O=AddTrust AB, C=SE
Valid = 2000-05-30 - 2020-05-30
:::
Subject = CN=AddTrust External CA Root, OU=AddTrust External TTP Network, O=AddTrust AB, C=SE
Issuer = CN=AddTrust External CA Root, OU=AddTrust External TTP Network, O=AddTrust AB, C=SE
Valid = 2000-05-30 - 2020-05-30
Trust Manager in Java
Finding Root CA in Java Trust Store
The client can traverse the chain up until it finds a root CA in its trust store.
Enumeration<String> trustStoreAliases = trustStore.aliases();
while (trustStoreAliases.hasMoreElements()) {
String tAlias = trustStoreAliases.nextElement();
X509Certificate rc = (X509Certificate)keyStore.getCertificate(tAlias);
if (rc.getIssuerX500Principal().equals(searchCert.getIssuerX500Principal())) {
System.err.println("Root CA found by name: " + rc.getIssuerDN());
printCert(rootCert);
// Proceed to validate the certificate chain using public keys and signatures
}
}
Validating Certificate Chain using TrustManager
Java provides java.security.X509TrustManager that implements the required functionality.
The following example overrides the default X509TrustManager with a LoggingX509TrustManager.
trustManager.checkServerTrusted(chain, "ECDHE_RSA");
import java.io.*;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.cert.*;
import java.security.cert.Certificate;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.*;
import javax.net.ssl.*;
public class CertTrust {
public static final DateTimeFormatter DF = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE.withZone( ZoneId.of("UTC") );
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String path = args[0];
String password = args[1];
String alias = args[2];
String trustPath = System.getProperties().get("java.home") + "/lib/security/cacerts";
KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
keyStore.load(new FileInputStream(new File(path)), password.toCharArray());
Certificate[] certificateChain = keyStore.getCertificateChain(alias);
X509Certificate[] chain = Arrays.stream(certificateChain).toArray(X509Certificate[]::new);
KeyStore trustStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
trustStore.load(new FileInputStream(trustPath), "changeit".toCharArray());
TrustManagerFactory factory = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());
factory.init(trustStore);
X509TrustManager defaultTrustManager = (X509TrustManager)factory.getTrustManagers()[0];
LoggingX509TrustManager loggingTrustManager = new LoggingX509TrustManager(defaultTrustManager, trustStore);
loggingTrustManager.checkServerTrusted(chain, "ECDHE_RSA");
}
public static class LoggingX509TrustManager implements X509TrustManager {
private X509TrustManager defaultTrustManager;
private KeyStore trustStore;
public LoggingX509TrustManager(X509TrustManager defaultTrustManager, KeyStore trustStore) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, KeyStoreException {
this.defaultTrustManager = defaultTrustManager;
this.trustStore = trustStore;
}
@Override
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException {
throw new CertificateException("not implemented");
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) throws CertificateException {
try {
CertPathValidator validator = CertPathValidator.getInstance("PKIX");
CertificateFactory factory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X509");
CertPath certPath = factory.generateCertPath(Arrays.asList(chain));
PKIXParameters params = new PKIXParameters(trustStore);
params.setRevocationEnabled(false);
validator.validate(certPath, params);
System.out.println("Certificate chain validated OK");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | InvalidAlgorithmParameterException | KeyStoreException | CertPathValidatorException e) {
System.err.println("Certificate chain validation failed: " + e + " : " + e.getCause());
}
try {
//check with default trust manager
defaultTrustManager.checkServerTrusted(chain, authType);
System.out.println("Default trust manager: certificate chain validated OK");
} catch (CertificateException ce){
System.err.println("Default trust manager: certificate chain validation failed: " + ce + " : " + ce.getCause());
}
}
@Override
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
return defaultTrustManager.getAcceptedIssuers();
}
}
}
Validation results for Expired Certificate:
Certificate chain validation failed: java.security.cert.CertPathValidatorException: timestamp check failed :
java.security.cert.CertificateExpiredException: NotAfter: Sat Mar 17 02:59:59 MSK 2018
Default trust manager: certificate chain validation failed:
sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path validation failed:
java.security.cert.CertPathValidatorException: timestamp check failed :
java.security.cert.CertPathValidatorException: timestamp check failed
Validation Results for Self-Signed Certificate:
Certificate chain validation failed: java.security.cert.CertPathValidatorException: Path does not chain with any of the trust anchors : null
Default trust manager: certificate chain validation failed: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed:
sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target
No TRUSTED root certificate found for CN=atsd.axibase.com, OU=Unknown, O=Unknown, L=Unknown, ST=Unknown, C=Unknown
Certificate Issuance
Self-Signed Certificate
Use keytool to generate and install a self-signed certificate.
The default certificate in ATSD is issued for 'atsd' CN and 'atsd' alias.
Example generating a self-signed certificate:
keytool -genkeypair -keystore /opt/atsd/atsd/conf/server.keystore -alias atsd -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 365000
Enter keystore password:
Re-enter new password:
What is your first and last name?
[Unknown]: atsd.axibase.com
What is the name of your organizational unit?
[Unknown]:
...
Is CN=atsd.axibase.com, OU=Unknown, O=Unknown, L=Unknown, ST=Unknown, C=Unknown correct?
[no]: yes
Enter key password for <atsd>
(RETURN if same as keystore password):
=== BEGIN chain ===
Subject = CN=atsd.axibase.com, OU=Unknown, O=Unknown, L=Unknown, ST=Unknown, C=Unknown
Issuer = CN=atsd.axibase.com, OU=Unknown, O=Unknown, L=Unknown, ST=Unknown, C=Unknown
Valid = 2018-04-12 - 3018-04-12
=== END chain ===
CA-Signed Certificate
Certificate authorities can perform various validation checks, from simple domain validation to extended legal and physical validation.
Domain validation is the easiest method to obtain an SSL certificate. It involves checks by the CA to prove that the requester has full control of a specific domain (range of domains in case of wildcard certificates).
Issuer: (CA ID: 1455)
commonName = COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA
...
Subject:
commonName = *.axibase.com
organizationalUnitName = PositiveSSL Wildcard
organizationalUnitName = Domain Control Validated
Before Let's Encrypt, this was accomplished by replying to a verification email sent to an inbox address recorded with the domain registrar (or from a shortlist).
This is the process to obtain certificates in 2015.
It is time consuming.
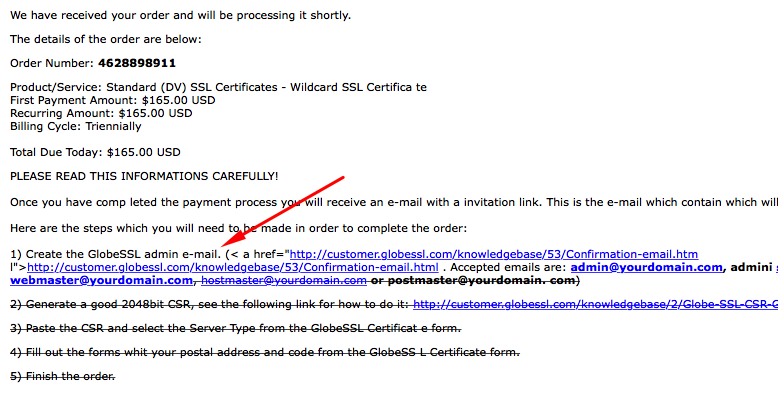
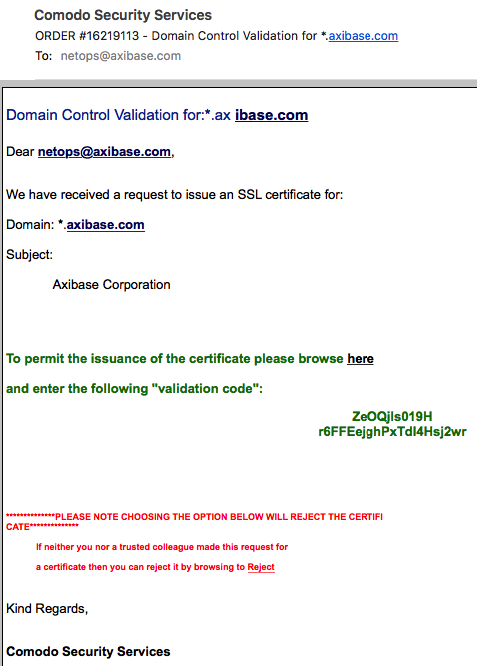
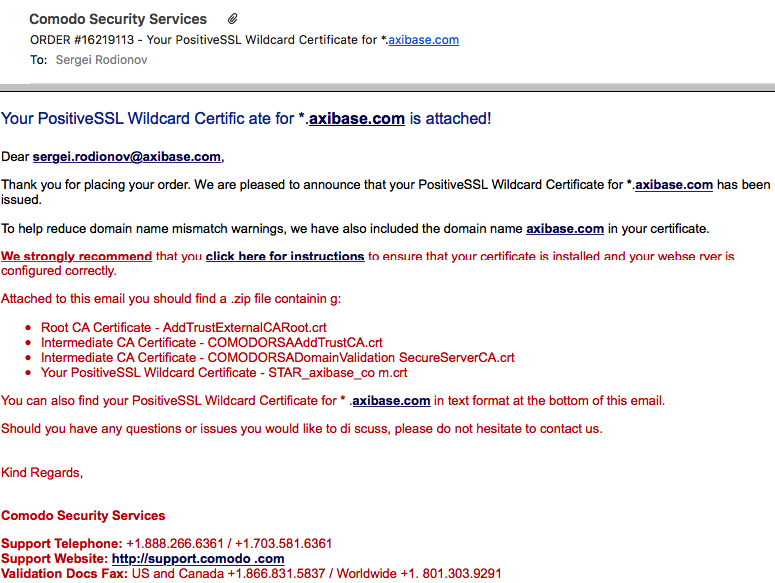
Custom CA-Signed Certificate
Creating a custom CA and signing 'end entity' certificates is possible but is of limited practical value given that such custom CA certificate is not present in the client trust stores.
Because any CA can sign any certificate it exposes clients to security risks (man-in-the-middle attack).
See Appendix on how to create a custom CA and sign any certificate.
Automated Certificate Issuance
ACME Protocol
The ACME (v1, v2) protocol used by Let's Encrypt supports the following challenge types for domain validation:
HOST-01. Certificate requester must respond to HTTP request on the requested domain to port 80.TLS-SNI-01. Certificate requester must respond to HTTPS request on the requested domain to port 443.DNS-01. Certificate requester must add an expiring TXT record to its DNS records on a nameserver.
The request must pass the challenge to receive the certificate.
The TLS-SNI-01 challenge on port 443 is no longer supported by Let's Encrypt.
Let's Encrypt Process
Automation with certbot
The process of obtaining certificates in 2018 using Let's Encrypt plugins and HOST-01 challenge.
sudo apt install software-properties-common
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
sudo apt update
sudo apt install certbot
nginx Mode
sudo apt install python-certbot-nginx
sudo certbot --nginx -d trends.axibase.com
- The certificate is only issued for 90 days.
- Port 80 must remain open for host challenge to succeed.
- Fix to port
80exposure is to configure nginx to redirect from80to443using301status. - Port
80exposure increases the risk of insecure cookie highjacking, for example in Redmine. - DNS validation is NOT possible for Axibase since the hosting provider Hostway does not provide an API for managing DNS.
Standalone Mode
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/certbot
sudo certbot certonly --standalone --agree-tos --no-eff-email --email support@axibase.com -w /var/www/certbot -d atsd.axibase.com
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/atsd.axibase.com/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/atsd.axibase.com/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2018-04-24. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot
again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run
"certbot renew"
- If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
The certificate files (including the chained certificates) and the private key are stored in the /etc/letsencrypt/live directory, each domain in its own sub-directory.
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/atsd.axibase.com
Renewal
- The certificate is issued only for 90 days.
- Port
80must remain open, or already be open using pre-hook, for renewals to work. - The certbot adds a
crontask to renew the certificate automatically. - Auto-renewal is triggered by
cronevery 12 hours with some jitter.
View certbot renewal command
cat /etc/cron.d/certbot
# /etc/cron.d/certbot: crontab entries for the certbot package
#
# Upstream recommends attempting renewal twice a day
#
# Eventually, this will be an opportunity to validate certificates
# haven't been revoked, etc. Renewal will only occur if expiration
# is within 30 days.
SHELL=/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
0 */12 * * * root test -x /usr/bin/certbot -a \! -d /run/systemd/system && perl -e 'sleep int(rand(3600))' && certbot -q renew
ATSD Integration
Initial Implementation
The initial integration of the ACME protocol in ATSD contained essentially the same functionality as certbot using acme4j client.
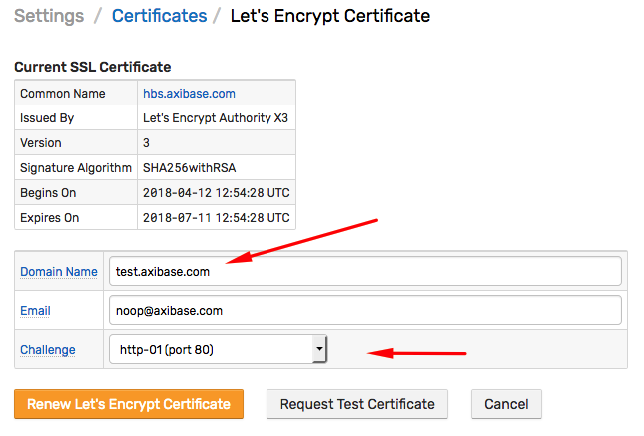
Implement HTTP and TLS challenges. The TLS challenge was then discontinued.
Estimate that most Axibase enterprise customers do not plan to adopt a centralized approach to automated certificate issuance using DNS challenge. The deployment of certbot on end nodes (hosts) is not necessary.
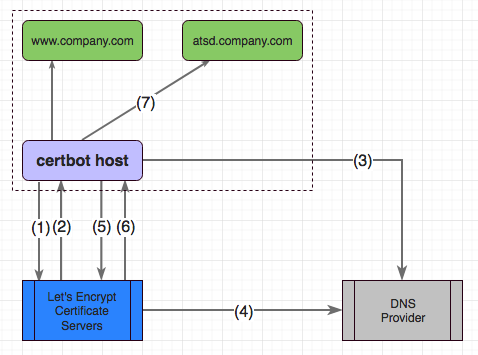
The certbot workflow in a centralized environment:
- (1) certbot initiates a new certificate challenge for
atsdsubdomain with Let's Encrypt servers - (2) Let's Encrypt server responds with a prepared DNS challenge
- (3) certbot invokes DNS provider API to add a temporary
TXTrecord - (4) Let's Encrypt servers validate the presence of
TXTrecord within a timeout - (5) certbot requests the new certificate from Let's Encrypt servers
- (6) Let's Encrypt servers reply with new certificates based on completed DNS challenge
- (7) certbot invokes deploy-hook to upload new certificates into ATSD
Certificate Upload Endpoint
To install new certificates into ATSD at runtime, upload the chained certificate and the private key into /admin/certificates/import/atsd endpoint in ATSD using curl.
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/atsd.axibase.com
sudo curl -k -u cert-renew:********** -X POST https://locahost:8443/admin/certificates/import/atsd \
-F "privkey=@privkey.pem" -F "fullchain=@fullchain.pem" -w "\n%{http_code}\n"
ATSD validates the certificate and install it without restarting the server.
Axibase upgraded Jetty to version 9.4 to support SSLContent reloading without reboot.
Upload Permissions
The /admin/certificates/import/atsd endpoint can be used by a user account with limited permissions:
- Role
USER. - No group membership.
- Allow access only from
127.0.0.1address.
Administrative permissions are not necessary.
Upload Restrictions
A non-trusted certificate can not replace the currently installed trusted certificate.
For instance, a self-signed certificate cannot be uploaded via the endpoint if the currently installed certificate is trusted by the default trust manager. Such a replacement must be performed manually and requires access to the local file system.
A new trusted certificate can replace the currently installed trusted certificate even if it involves a change in the common name.
Renewal Trigger
To automate the certificate upload after certbot renewal, create deploy.sh script.
The certbot can be installed on the same machine as ATSD or on a remote machine in which case its IP address must be included in the "Allow Access" list.
#!/bin/bash
axiuser=cert-renew
axipass=**********
atsd_host=localhost
atsd_port=8443
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/atsd.axibase.com/
curl -k -u $axiuser:$axipass https://localhost:8443/admin/certificates/import/atsd -F "privkey=@privkey.pem" -F "fullchain=@fullchain.pem" -w "\n%{http_code}\n"
Add post-renewal trigger to the renewal command.
crontab -e
0 */12 * * * certbot -q renew --deploy-hook "/path/to/deploy.sh"
Renewal Demo
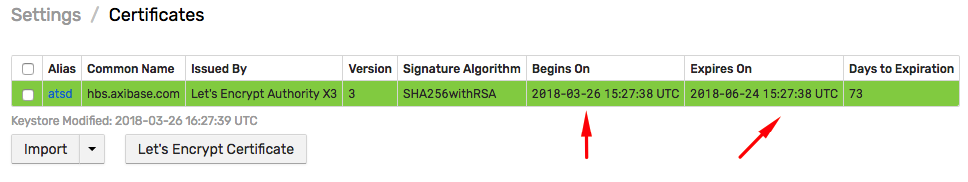
Certificates are displayed on Settings > Certificates page.
sudo certbot renew
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/hbs.axibase.com.conf
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cert not yet due for renewal
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following certs are not due for renewal yet:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/hbs.axibase.com/fullchain.pem expires on 2018-06-24 (skipped)
No renewals were attempted.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Review renewal logs if necessary.
sudo cat /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/hbs.axibase.com.conf
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cert not due for renewal, but simulating renewal for dry run
Plugins selected: Authenticator standalone, Installer None
Renewing an existing certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for hbs.axibase.com
Waiting for verification...
Cleaning up challenges
Dry run: skipping deploy hook command: /home/axibase/certbot-hook/deploy.sh
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
new certificate deployed without reload, fullchain is
/etc/letsencrypt/live/hbs.axibase.com/fullchain.pem
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates below have not been saved.)
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/hbs.axibase.com/fullchain.pem (success)
** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates above have not been saved.)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To check that deploy-hook is configured, search for it in the /etc/letsencrypt directory.
sudo grep -nr /etc/letsencrypt -e "deploy.sh"
/etc/letsencrypt/renewal/hbs.axibase.com.conf:14:renew_hook = /home/axibase/certbot-hook/deploy.sh
Force Renewal
Renewals are subject to weekly limits, per subdomain and per domain.
sudo certbot renew --force-renewal
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/hbs.axibase.com.conf
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Plugins selected: Authenticator standalone, Installer None
Renewing an existing certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for hbs.axibase.com
Waiting for verification...
Cleaning up challenges
Running deploy-hook command: /home/axibase/certbot-hook/deploy.sh
Output from deploy.sh:
Upload private key and certificate
The script reports an error because the curl connection is closed when the SSL context is restarted. While all current SSL connections are closed, ATSD server itself is not restarted during this process.
Error output from deploy.sh:
* Trying 127.0.0.1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0* Connected to localhost (127.0.0.1) port 8443 (#0)
* Cipher selection: ALL:!EXPORT:!EXPORT40:!EXPORT56:!aNULL:!LOW:!RC4:@STRENGTH
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
CApath: none
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
} [290 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
{ [85 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
{ [2472 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12):
{ [413 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server finished (14):
{ [4 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16):
} [150 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
} [1 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
} [16 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
{ [1 bytes data]
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
{ [16 bytes data]
* SSL connection using TLSv1.2 / ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
* Server certificate:
* subject: CN=hbs.axibase.com
* start date: Mar 26 15:27:38 2018 GMT
* expire date: Jun 24 15:27:38 2018 GMT
* issuer: C=US; O=Let's Encrypt; CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3
* SSL certificate verify ok.
* Server auth using Basic with user 'cert-renew'
> POST /admin/certificates/import/atsd HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8443
> Authorization: Basic *************************
> User-Agent: curl/7.50.2
> Accept: */*
> Content-Length: 5876
> Expect: 100-continue
> Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=------------------------d379b7cc72088a1e
>
< HTTP/1.1 100 Continue
} [158 bytes data]
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Date: Thu, 12 Apr 2018 13:54:29 GMT
< Expires: Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 GMT
< Vary: Accept-Encoding, User-Agent
< Content-Length: 0
< Server: Jetty(9.4.z-SNAPSHOT)
<
* Curl_http_done: called premature == 0
100 5876 0 0 100 5876 0 19870 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 19986
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
new certificate deployed without reload, fullchain is
/etc/letsencrypt/live/hbs.axibase.com/fullchain.pem
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/hbs.axibase.com/fullchain.pem (success)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
New certificate is now installed. No ATSD restart performed.
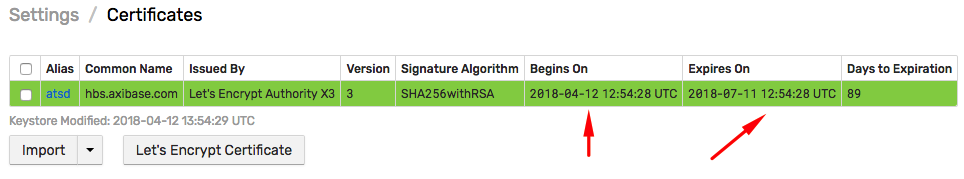
Public Certificate Logging
Certificate Transparency Logs
Some CAs, including Let's Encrypt, voluntarily disclose all issued certificates to one or multiple 'Certificate Transparency' servers.
CT servers store immutable logs of certificate issuance events which contain the subject CN (common name) and certificate details.
The CT servers also accept events from crawlers when they identify a new certificate.
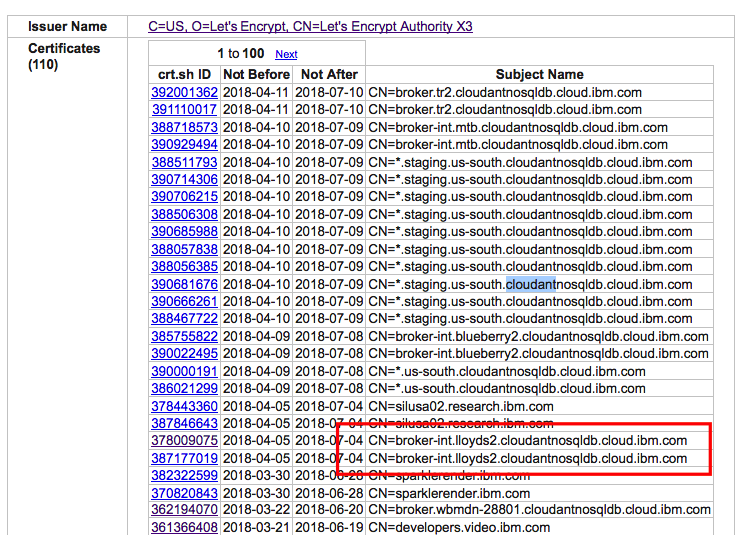
crt.sh (https://crt.sh) is a front-end to a database of issued certificates, maintained by COMODO CA.
Certificate chain for the old wildcard certificate:
*.axibase.com
issued by COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA
issued by COMODO RSA Certification Authority
issued by AddTrust External CA Root [ROOT]
- 6871548 (
https://crt.sh/?id=6871548) --1455 (https://crt.sh/?caid=1455)----3509153 (https://crt.sh/?id=3509153)------1044348 (https://crt.sh/?id=1044348)
Certificate details including DNS names are now publicly available even if the certificate is issued for an internal server:
- trends.axibase.com CT log
crt.sh maintained by one of the CAs, COMODO, allows searching a consolidated log from multiple CT servers for certificates using wildcards.
axibase.comcertificates (https://crt.sh/?Identity=%.axibase.com)
CRT Database Access
Publicly-accessible certificate database.
Table schema is available on GitHub.
Database.URL = jdbc:postgresql://crt.sh:5432/certwatch
Username = guest
Password = (none)
SELECT ci.ISSUER_CA_ID,
ca.NAME ISSUER_NAME,
ci.NAME_VALUE NAME_VALUE,
min(c.ID) MIN_CERT_ID,
min(ctle.ENTRY_TIMESTAMP) MIN_ENTRY_TIMESTAMP,
x509_notBefore(c.CERTIFICATE) NOT_BEFORE,
x509_notAfter(c.CERTIFICATE) NOT_AFTER
FROM ca,
ct_log_entry ctle,
certificate_identity ci,
certificate c
WHERE ci.ISSUER_CA_ID = ca.ID
AND c.ID = ctle.CERTIFICATE_ID
AND (reverse(lower(ci.NAME_VALUE)) LIKE reverse(lower('%.axibase.com')) OR reverse(lower(ci.NAME_VALUE)) = reverse(lower('axibase.com')))
AND ci.NAME_TYPE = 'commonName'
AND ci.CERTIFICATE_ID = c.ID
AND CAST(x509_notBefore(c.CERTIFICATE) AS Date) >= '2018-04-01'
GROUP BY c.ID, ci.ISSUER_CA_ID, ISSUER_NAME, NAME_VALUE
ORDER BY MIN_ENTRY_TIMESTAMP DESC, NAME_VALUE, ISSUER_NAME;
| issuer_ca_id | issuer_name | name_value | min_cert_id | min_entry_timestamp | not_before | not_after |
|--------------|-------------------------------------------------------|---------------------|-------------|---------------------------|---------------------------|--------------------------|
| 16418 | C=US, O=Let's Encrypt, CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3 | trends.axibase.com | 382036307 | 2018-04-06T21:26:08.180Z | 2018-04-03T10:55:24.000Z | 2018-07-02T10:55:24.000Z |
| 16418 | C=US, O=Let's Encrypt, CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3 | trends.axibase.com | 375329448 | 2018-04-03T11:55:24.257Z | 2018-04-03T10:55:24.000Z | 2018-07-02T10:55:24.000Z |
- Query Performance
The database is slow for analytical queries (GROUP BY). Analytical queries do not complete.
ChartLab crt.sh Portal.
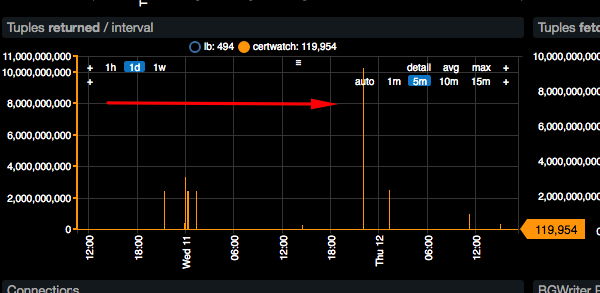
Certificate Issuance Monitoring
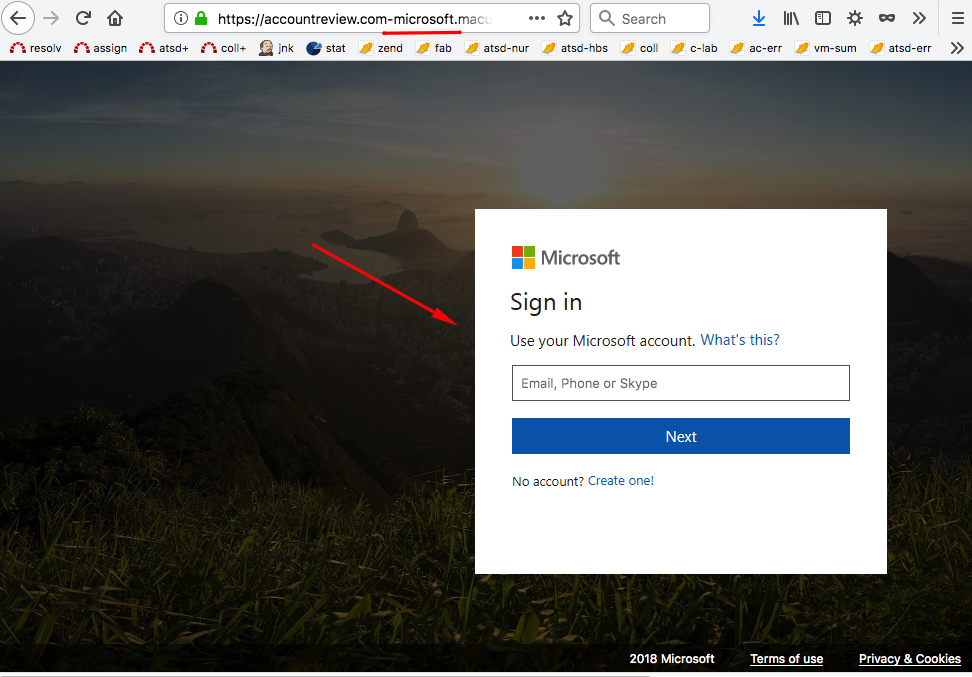
Bank of america phishing sites:
https://crt.sh/?q=bankofamerica%25Sample phishing domains:
accountreview.com-microsoft.macultiple .galichnyj-kabinet-sberbank .ru
Custom CA
Generate Custom CA Certificate
Generate private key file for the new custom CA which is manually added to the trust stores. This key needs to guarded as top secret.
openssl genrsa -des3 -out axibase_root_ca.key 2048
Generate root CA certificate. This certificate is used to sign (validate) end entity certificates.
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key axibase_root_ca.key -sha256 -days 90 -out axibase_root_ca.pem
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:US
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:CA
Locality Name (eg, city) []:Cupertino
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:Axibase Corporation
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:SWG
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:Axibase Root CA
Email Address []:
Convert PEM file to CRT file.
openssl x509 -outform der -in axibase_root_ca.pem -out axibase_root_ca.crt
Install Custom CA Certificate
Operating System
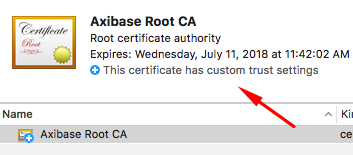
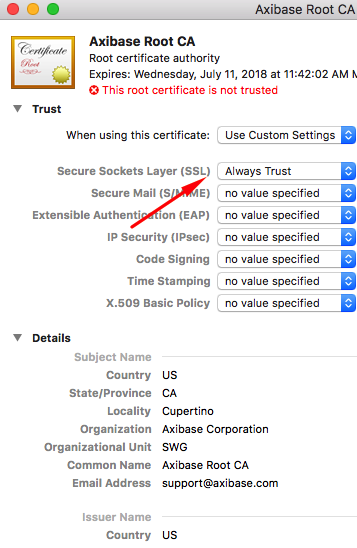
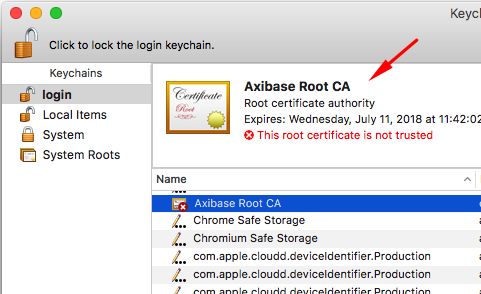
Browser
- Chrome and Safari
These browsers inherit root CAs from the operating system trust store.
- Firefox Browser
Firefox displays an Unknown Identity error.
Import Axibase Root CA via Settings > Security and Privacy.
Java
Root CAs are stored in /jre/lib/security/cacerts.
List current root CA in JRE:
keytool -list -keystore /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_131.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/security/cacerts
Add 'Axibase Root CA' to root CAs (need root privilege).
sudo keytool -keystore /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_131.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/security/cacerts \
-importcert -alias axibaserootca -file axibase_root_ca.crt
Notice the CA:true flag.
Enter keystore password:
Owner: CN=Axibase Root CA, OU=SWG, O=Axibase Corporation, L=Cupertino, ST=CA, C=US
Issuer: CN=Axibase Root CA, OU=SWG, O=Axibase Corporation, L=Cupertino, ST=CA, C=US
Serial number: db9a0b3b2639f4f9
Valid from: Thu Apr 12 11:42:02 MSK 2018 until: Wed Jul 11 11:42:02 MSK 2018
...
Extensions:
#2: ObjectId: 2.5.29 Criticality=false
BasicConstraints:[
CA:true
PathLen:2147483647
]
Trust this certificate? [no]: yes
Certificate was added to keystore
Verify that 'Axibase Root CA' is present in the root CA list.
keytool -list -keystore /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_131.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/security/cacerts | grep axibase
axibaserootca, Apr 12, 2018, trustedCertEntry,
Custom CA Examples
ATSD Validated by Custom CA
Generate Certificate Signing Request for Domain
Generate private key file.
openssl genrsa -out atsd_axibase_com.key 2048
Generate CSR (Certificate Signing Request) file, to be submitted to the CA.
openssl req -new -key atsd_axibase_com.key -out atsd_axibase_com.csr
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:US
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:CA
Locality Name (eg, city) []:Cupertino
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:Axibase Corporation
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:SWG
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:atsd.axibase.com
Submit the CSR file atsd_axibase_com.csr to the CA.
CA signs CSR for the domain
openssl x509 -req -in atsd_axibase_com.csr -CAcreateserial \
-CA axibase_root_ca.pem -CAkey axibase_root_ca.key \
-out atsd_axibase_com.crt -days 90 -sha256 -extfile atsd_axibase_com.conf
Extended settings (CA:FALSE).
cat atsd_axibase_com.conf
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage=serverAuth
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = atsd.axibase.com
Create atsd KeyStore
Create trust store file in PKCS12 format containing the atsd_axibase_com private key and the signed certificate, stored under 1 (default) alias.
openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey atsd_axibase_com.key -in atsd_axibase_com.crt -out atsd_axibase_com.pkcs12
Convert the PKCS12 keystore into JKS keystore, change alias from 1 to atsd.
keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore atsd_axibase_com.pkcs12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -alias 1 -destkeystore atsd_axibase_com.keystore -destalias atsd
Check atsd_axibase_com.keystore: chain and trust.
alias= atsd
trust.path= /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_131.jdk/Contents/Home/jre//lib/security/cacerts
keystore aliases= [atsd]
=== BEGIN chain ===
Subject = CN=atsd.axibase.com, OU=SWG, O=Axibase Corporation, L=Cupertino, ST=CA, C=US
Issuer = CN=Axibase Root CA, OU=SWG, O=Axibase Corporation, L=Cupertino, ST=CA, C=US
Valid = 2018-04-12 - 2018-07-11
:::
=== END chain ===
Certificate chain validated OK
Default trust manager: certificate chain validated OK
The atsd_axibase_com certificate, signed with 'Axibase Root CA' is now valid.
If Axibase Root CA is not present in the trust store, an exception is raised:
Certificate chain validatation failed: java.security.cert.CertPathValidatorException: Path does not chain with any of the trust anchors : null
Default trust manager: certificate chain validatation failed: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed:
sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target : sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target
No TRUSTED root certificate found for CN=Axibase Root CA, OU=SWG, O=Axibase Corporation, L=Cupertino, ST=CA, C=US
Deploy atsd KeyStore into ATSD
Start ATSD container.
docker run -d --name=atsd -p 8443:8443 axibase/atsd:latest
docker exec -it atsd bash
Copy atsd_axibase_com.keystore as /opt/atsd/atsd/conf/server.keystore and set correct file permissions.
docker cp atsd_axibase_com.keystore atsd:/opt/atsd/atsd/conf/server.keystore
docker exec -u root atsd chown axibase:axibase /opt/atsd/atsd/conf/server.keystore
Restart ATSD
docker exec /opt/atsd/bin/atsd-tsd.sh stop
docker exec /opt/atsd/bin/atsd-tsd.sh start
Change DNS for atsd.axibase.com
Modify /etc/hosts File to Route atsd.axibase.com to localhost
sudo nano /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost, atsd.axibase.com
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
fe80::1%lo0 localhost
Access ATSD on a trusted certificate
The atsd.axibase.com domain is trusted because its certificate is signed by 'Axibase Root CA' which is present in MacOS System Root list.
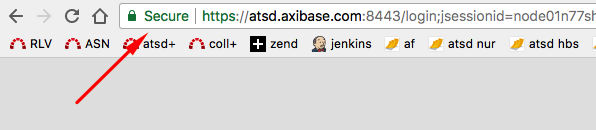
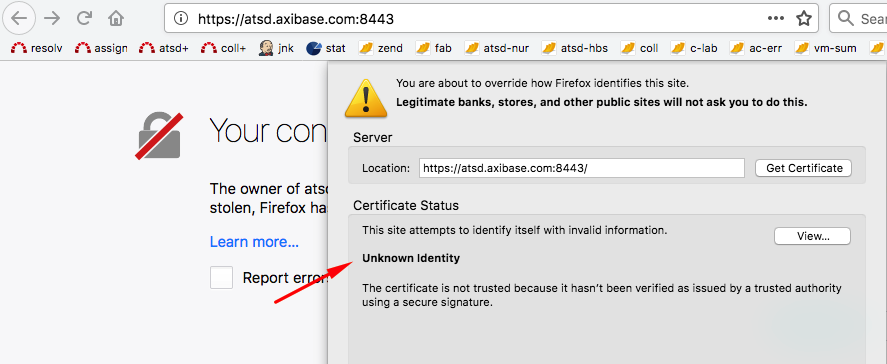
Firefox displays an 'Unknown Identity' error.
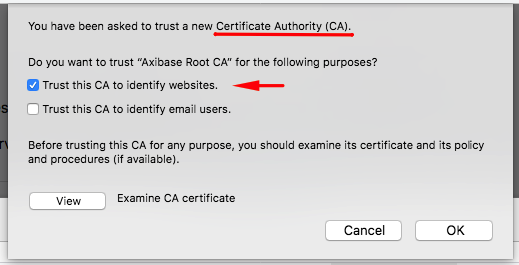
Import 'Axibase Root CA' via Settings > Security and Privacy.
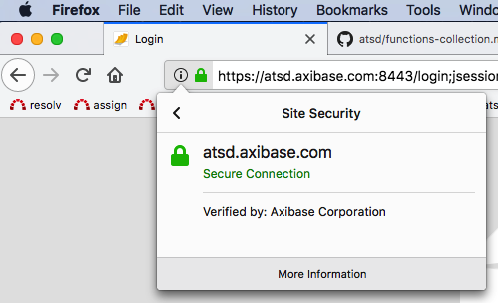
The certificate is now validated.
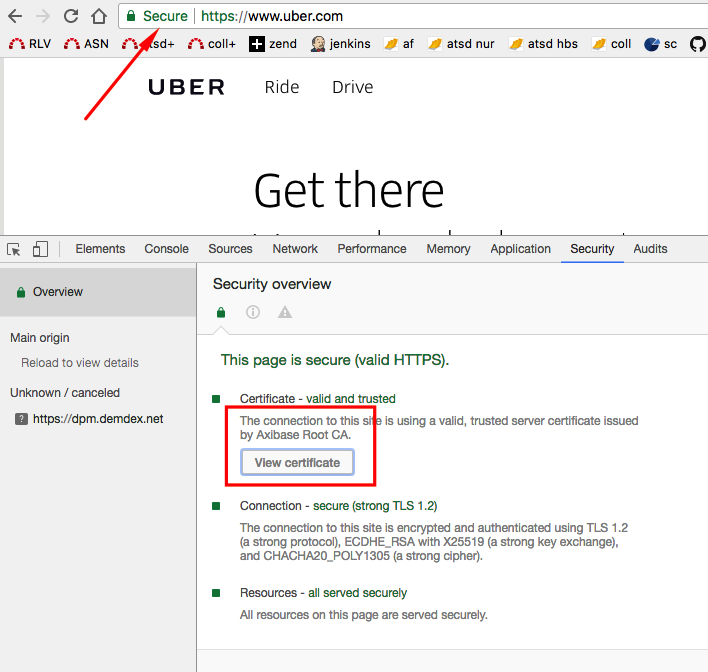
Any Site Validated by Custom CA
Example: https://www.uber.com
Change DNS
Modify /etc/hosts File to route www.uber.com to localhost
sudo nano /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost, www.uber.com
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
fe80::1%lo0 localhost
Generate SSL Certificate Request
Generate private key file
openssl genrsa -out www.uber.com.key 2048
Generate CSR
openssl req -new -key www.uber.com.key -out www.uber.com.csr
...
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:US
...
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:www.uber.com
Sign CSR
openssl x509 -req -in www.uber.com.csr -CAcreateserial \
-CA axibase_root_ca.pem -CAkey axibase_root_ca.key \
-out www.uber.com.crt -days 90 -sha256 -extfile www.uber.com.conf
Launch nginx Proxy Container
docker run --name uber -d -p 443:443 -e VIRTUAL_HOST=www.uber.com -v /Users/sergei/Desktop/cert:/etc/nginx/certs -v /var/run/docker.sock:/tmp/docker.sock:ro jwilder/nginx-proxy
docker exec -it uber bash
apt update && apt install nano
Modify nginx server configuration to fetch (proxy) content from https://uber.com for all requests.
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
...
location / {
proxy_pass https://uber.com;
}
}
Apply new nginx configuration without restarting.
service nginx reload
Access https://www.uber.com in the browser as usual.

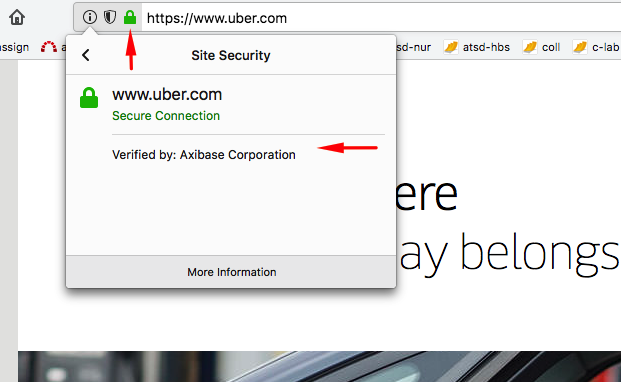
The requests are now logged in nginx. Content is proxied from https://uber.com.
nginx.1 | www.uber.com 172.17.0.1 - - [12/Apr/2018:10:55:27 +0000] "GET / HTTP/2.0" 200 162485 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/65.0.3325.181 Safari/537.36"
nginx.1 | www.uber.com 172.17.0.1 - - [12/Apr/2018:10:55:30 +0000] "GET /api/current-city HTTP/2.0" 200 174 "https://www.uber.com/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/65.0.3325.181 Safari/537.36"
Since custom CA is in the Java trust store, URL connections complete without errors as well.
URL url = new URL("https://www.uber.com:443/");
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.connect();
System.out.println("Connection OK");
Connection OK
If the certificate is untrusted, you see this error:
Exception in thread "main" javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: java.security.cert.CertificateException: No name matching www.uber.com found
at sun.security.ssl.Alerts.getSSLException(Alerts.java:192)
Miscellaneous
openssl s_client Utility
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect axibase.com:443
CONNECTED(00000003)
depth=2 O = Digital Signature Trust Co., CN = DST Root CA X3
verify return:1
depth=1 C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = Let's Encrypt Authority X3
verify return:1
depth=0 CN = axibase.com
verify return:1
---
Certificate chain
0 s:/CN=axibase.com
i:/C=US/O=Let's Encrypt/CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIFCjCCA/KgAwIBAgISA5CuzM7UVH6hkig+pFXVBagZMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUA
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
1 s:/C=US/O=Let's Encrypt/CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3
i:/O=Digital Signature Trust Co./CN=DST Root CA X3
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIEkjCCA3qgAwIBAgIQCgFBQgAAAVOFc2oLheynCDANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADA/
...
KOqkqm57TH2H3eDJAkSnh6/DNFu0Qg==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
---
Server certificate
subject=/CN=axibase.com
issuer=/C=US/O=Let's Encrypt/CN=Let's Encrypt Authority X3
---
No client certificate CA names sent
Peer signing digest: SHA512
Server Temp Key: ECDH, P-256, 256 bits
---
SSL handshake has read 3146 bytes and written 431 bytes
---
New, TLSv1/SSLv3, Cipher is ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
Server public key is 2048 bit
Secure Renegotiation IS supported
Compression: NONE
Expansion: NONE
No ALPN negotiated
SSL-Session:
Protocol : TLSv1.2
Cipher : ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
Session-ID: D63A3B9080395F810EAFECB6E979E4398471DDE539373573282C9425957C537D
Session-ID-ctx:
Master-Key: 523E253B06B67151C8BD2887F6BA344FA5E8E7921B0429BCB7A4B5151D2AB8430FD7C1B46CCEDB1AD6451944F110EBB6
Key-Arg : None
PSK identity: None
PSK identity hint: None
SRP username: None
TLS session ticket lifetime hint: 300 (seconds)
TLS session ticket:
0000 - a9 1c 11 e0 57 95 47 33-8f 0b ff ed 7e ff 60 ad ....W.G3....~.`.
...
Start Time: 1523343252
Timeout : 300 (sec)
Verify return code: 0 (ok)
---
Java Client Debugging
The Java clients use a variety of methods to establish SSL connections and execute requests over the HTTPS protocol.
To debug SSL connectivity issues such as SSL handshake failures, enable the javax.net.debug parameter.
java -Djavax.net.debug=ssl
The ssl output can be further detailed by appending one of the following options, for example javax.net.debug=ssl:trustmanager:
recordhandshakekeygensessiondefaultctxsslctxsessioncachekeymanagertrustmanager
Refer to IBMJSSE2 tracing note for additional details.
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DH_anon_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DH_anon_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_anon_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DH_anon_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
Ignoring unavailable cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
trustStore is: /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_131.jdk/Contents/Home/jre/lib/security/cacerts
trustStore type is : jks
trustStore provider is :
init truststore
adding as trusted cert:
Subject: CN=Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA-1, O=Equifax Secure Inc., C=US
Issuer: CN=Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA-1, O=Equifax Secure Inc., C=US
Algorithm: RSA; Serial number: 0xc3517
Valid from Mon Jun 21 08:00:00 MSD 1999 until Mon Jun 22 07:00:00 MSK 2020
...
trigger seeding of SecureRandom
done seeding SecureRandom
Allow unsafe renegotiation: false
Allow legacy hello messages: true
Is initial handshake: true
Is secure renegotiation: false
main, setSoTimeout(30000) called
main, setSoTimeout(30000) called
Ignoring disabled protocol: SSLv3
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 for TLSv1
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 for TLSv1
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 for TLSv1
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 for TLSv1
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 for TLSv1
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 for TLSv1
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 for TLSv1
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
Ignoring unsupported cipher suite: TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
%% No cached client session
*** ClientHello, TLSv1
RandomCookie: GMT: 1507311304 bytes = { 166, 106, 123, 5, 109, 113, 69, 36, 17, 27, 114, 137, 94, 204, 178, 231, 12, 131, 55, 208, 175, 127, 222, 187, 100, 208, 141, 168 }
Session ID: {}
Cipher Suites: [TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, SSL_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, SSL_DHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, SSL_DHE_DSS_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, TLS_EMPTY_RENEGOTIATION_INFO_SCSV]
Compression Methods: { 0 }
Extension elliptic_curves, curve names: {secp256r1, secp384r1, secp521r1, sect283k1, sect283r1, sect409k1, sect409r1, sect571k1, sect571r1, secp256k1}
Extension ec_point_formats, formats: [uncompressed]
Extension server_name, server_name: [type=host_name (0), value=nur.axibase.com]
***
main, WRITE: TLSv1 Handshake, length = 131
main, READ: TLSv1.2 Alert, length = 2
main, RECV TLSv1.2 ALERT: fatal, handshake_failure
main, called closeSocket()
main, handling exception: javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: Received fatal alert: handshake_failure
main, called close()
main, called closeInternal(true)
main, called close()
main, called closeInternal(true)
main, called close()
main, called closeInternal(true)
Exception in thread "main" javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: Received fatal alert: handshake_failure
