Installation: Amazon Elastic MapReduce (EMR)
Overview
The document describes how to deploy ATSD on HBase with AWS S3 as the underlying file system.
Operational Advantages
- Scale storage and compute layers independently to handle a variety of use cases, including the small cluster/large dataset scenario.
- Dynamically adjust the number of region servers based on auto-scaling rules.
- Simplified backup and recovery.
- Reduced storage footprint. No need for
3-xdata replication and additional disk space required for HFile compactions. - Increased resilience based on AWS S3 reliability and durability.
- Read-only cluster replicas.
Create S3 Bucket
Create the S3 bucket prior to installation. The bucket, named atsd in the example below, stores the hbase-root directory and contains both metadata and HFiles.
aws s3 mb s3://atsd
If necessary, the hbase-root directory is created by HBase when the cluster is started for the first time. The directory is not deleted when the cluster is stopped.
Check the contents of the S3 bucket prior to launching the cluster.
aws s3 ls --summarize --human-readable --recursive s3://atsd
Download Distribution Files
- Amazon EMR
5.0.x-5.3.xwith HBase1.2.x
curl -o atsd-cluster.tar.gz https://axibase.com/public/atsd-cluster.tar.gz
- Amazon EMR
5.12.x-5.17.xwith HBase1.4.x
curl -o atsd-cluster.tar.gz https://axibase.com/public/aws/atsd-cluster-1.4.x.tar.gz
Refer to AWS EMR Release Notes for more information.
Deploy Co-processor
Extract atsd-hbase.$REVISION.jar from the archive.
tar -xvf atsd-cluster.tar.gz atsd/atsd-hbase*jar
Co-processors
The atsd-hbase.$REVISION.jar file contains ATSD filters and procedures invoked by ATSD on each node in the HBase cluster for optimized data processing.
To make ATSD packages loadable by region servers at start time, copy the JAR file to the directory specified in the HBase configuration variable hbase.dynamic.jars.dir which is set to hbase.rootdir/lib by default. If the HBase root directory is s3://atsd/hbase-root, the target directory is s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib.
aws s3 cp atsd/atsd-hbase.*.jar s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
The
cpcommand removes the revision from theatsd-hbase.$REVISION.jarfile to avoid changingcoprocessor.jarsetting in theserver.propertiesfile each time when the JAR file is upgraded.
Verify that the copied file is stored as atsd-hbase.jar in the hbase-root/lib directory in S3.
aws s3 ls --summarize --human-readable --recursive s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib
2018-08-31 21:43:24 555.1 KiB hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
Total Objects: 1
Total Size: 555.1 KiB
Launch Cluster
Copy the AWS CLI cluster launch command into an editor.
export CLUSTER_ID=$( \
aws emr create-cluster \
--name "ATSD HBase" \
--applications Name=HBase \
--release-label emr-5.3.1 \
--output text \
--use-default-roles \
--ec2-attributes KeyName=<key-name>,SubnetId=<subnet> \
--instance-groups \
Name=Master,InstanceCount=1,InstanceGroupType=MASTER,InstanceType=m4.large \
Name=Region,InstanceCount=3,InstanceGroupType=CORE,InstanceType=m4.large \
--configurations '[{
"Classification": "hbase",
"Properties": { "hbase.emr.storageMode": "s3" }
},{
"Classification": "hbase-site",
"Properties": { "hbase.rootdir": "s3://atsd/hbase-root" }
}]' \
)
Choose EMR Version
Replace emr-5.3.1 release label with the correct version:
emr-5.3.1for HBase1.2.xemr-5.17.1for HBase1.4.x
Specify Network Parameters
Replace <key-name> and <subnet> parameters.
The <key-name> parameter corresponds to the name of the private key used to log in to cluster nodes.
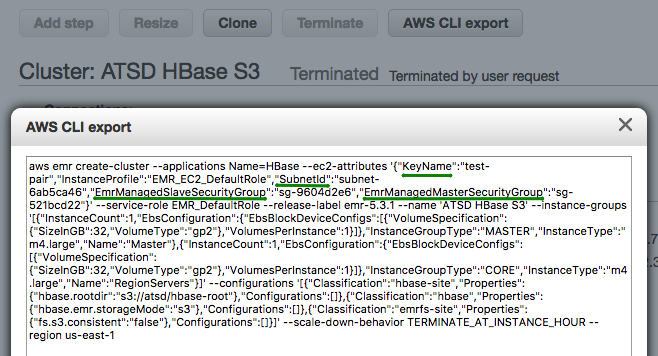
The <subnet> parameter is required when launching particular instance types. To discover the correct subnet for your account, launch a sample cluster manually in the AWS EMR Console and review the settings using AWS CLI export.
--ec2-attributes KeyName=ec2-pkey,SubnetId=subnet-6ab5ca46,EmrManagedMasterSecurityGroup=sg-521bcd22,EmrManagedSlaveSecurityGroup=sg-9604d2e6 \
Set Cluster Size
Adjust EC2 instance types and total instance count for the RegionServers group as needed. Review AWS documentation for additional settings.
Tip
Cluster size can be adjusted at runtime, without restarting the service.
The minimum number of nodes in each instance group is 1, therefore the smallest EMR cluster can have two EC2 instances:
Name=Master,InstanceCount=1,InstanceGroupType=MASTER,InstanceType=m4.large \
Name=Region,InstanceCount=1,InstanceGroupType=CORE,InstanceType=m4.large \
Enable Consistent View
For long-running production clusters, enable EMR Consistent View, which identifies inconsistencies in S3 object listings and resolves them using retries with exponential timeouts. When this option is enabled, the HBase metadata is also stored in a DynamoDB table.
Checks are enabled by adding the Consistent setting to the launch command.
--emrfs Consistent=true,Args=[fs.s3.consistent.metadata.tableName=EmrFSMetadata] \
Avoid DynamoDB table name conflicts
The EMR service does not automatically remove the specified DynamoDB table when a cluster is stopped. Delete the table manually after the cluster is deleted. When running multiple clusters concurrently, ensure that each cluster uses a different DynamoDB table name to avoid collision. The default table name is EmrFSMetadata.
Launch Cluster
Launch the cluster by executing the above command. The command returns a cluster ID and stores it as an environment variable.
Verify HBase Status
Log in to Master Node
Monitor cluster status until the bootstrapping process is complete.
watch 'aws emr describe-cluster --cluster-id $CLUSTER_ID | grep MasterPublic | cut -d "\"" -f 4'
Determine the public IP address of the HBase Master node.
export MASTER_IP=$(aws emr describe-cluster --cluster-id $CLUSTER_ID | grep MasterPublic | cut -d "\"" -f 4) \
&& echo $MASTER_IP
Specify path to private SSH key and log in to the node.
ssh -i /path/to/<key-name>.pem -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no hadoop@$MASTER_IP
Wait until HBase services are running on the HMaster node.
watch 'initctl list | grep hbase'
hbase-thrift start/running, process 8137
hbase-rest start/running, process 7842
hbase-master start/running, process 7987
Verify HBase version (1.2.x or 1.4.x) and re-run the status command until the cluster becomes operational.
echo "status" | hbase shell
Wait until the cluster initializes and the Master is initializing message is no longer visible.
status
1 active master, 0 backup masters, 4 servers, 0 dead, 1.0000 average load
Install ATSD
Log in to the server where you plan to install ATSD. For testing and development, you can co-install ATSD on the HMaster node.
ssh -i /path/to/<key-name>.pem ec2-user@$PUBLIC_IP
Verify that JDK 8 is installed on the server.
javac -version
java version
Change to a volume with at least 10 GB of available disk space.
df -h
cd /mnt
Download ATSD distribution files as described above. Extract the files from archive.
tar -xvf atsd-cluster.tar.gz
Set path to Java 8 in the ATSD start script.
JP=`dirname "$(dirname "$(readlink -f "$(which javac || which java)")")"` \
&& sed -i "s,^export JAVA_HOME=.*,export JAVA_HOME=$JP,g" atsd/atsd/bin/start-atsd.sh \
&& echo $JP
If installing ATSD on an HMaster node where ports are already in use, change the default ATSD port numbers to 9081, 9082, 9084, 9088, and 9443, respectively.
sed -i 's/=.*80/=90/g; s/=.*8443/=9443/g' atsd/atsd/conf/server.properties \
&& grep atsd/atsd/conf/server.properties -e "port"
Set path to ATSD coprocessor file.
echo "coprocessors.jar=s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar" >> atsd/atsd/conf/server.properties \
&& grep atsd/atsd/conf/server.properties -e "coprocessors.jar"
Check server.properties file to verify that coprocessors.jar setting and port numbers are set correctly.
cat atsd/atsd/conf/server.properties
Sample server.properties file.
#
# HBase settings
#
hbase.compression.type = gz
hbase.table.prefix=atsd_
messages.timeToLive=31536000
#
# Network Settings
#
input.port = 9081
udp.input.port = 9082
pickle.port = 9084
http.port = 9088
https.port=9443
https.keyStorePassword=****
https.keyManagerPassword=****
https.trustStorePassword=
coprocessors.jar=s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
Check memory usage and increase ATSD JVM memory to 50% of total physical memory installed in the server, if available.
free
nano atsd/atsd/conf/atsd-env.sh
JAVA_OPTS="-server -Xmx4000M -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath="$atsd_home"/logs"
Open Hadoop properties file and specify HMaster hostname.
nano atsd/atsd/conf/hadoop.properties
# localhost if co-installing ATSD on HMaster
hbase.zookeeper.quorum = 192.0.2.1
Start ATSD.
./atsd/atsd/bin/start-atsd.sh
Monitor startup progress using the log file.
tail -f atsd/atsd/logs/atsd.log
It can take ATSD several minutes to create tables after initializing the system.
...
2018-08-31 22:10:37,890;INFO;main;org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;FrameworkServlet 'dispatcher': initialization completed in 3271 ms
...
2018-08-31 22:10:37,927;INFO;main;org.eclipse.jetty.server.AbstractConnector;Started SelectChannelConnector@0.0.0.0:9088
2018-08-31 22:10:37,947;INFO;main;org.eclipse.jetty.util.ssl.SslContextFactory;Enabled Protocols [TLSv1, TLSv1.1, TLSv1.2] of [SSLv2Hello, SSLv3, TLSv1, TLSv1.1, TLSv1.2]
2018-08-31 22:10:37,950;INFO;main;org.eclipse.jetty.server.AbstractConnector;Started SslSelectChannelConnector@0.0.0.0:9443
Log in to the ATSD web interface at https://atsd_hostname:8443. Modify the URL if the HTTPS port is customized.
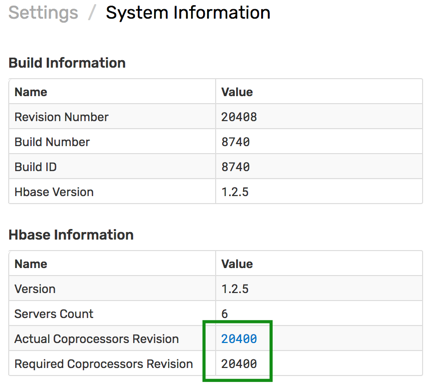
Open the Settings > System Information page and verify that the co-processor file is compatible with the ATSD version.
Upgrading
Replace Co-processor File
Download the archive containing the latest ATSD version to the machine with access to S3. Choose the correct download URL based on your Amazon EMR version.
Copy the co-processor jar file as described in the installation procedure.
Restart the HBase cluster.
Replace ATSD Executable File
Log in to the server where ATSD is installed.
Download the latest ATSD distribution files as described above. Extract the files from archive.
tar -xvf atsd-cluster.tar.gz
Stop ATSD.
/path/to/atsd/atsd/bin/stop-atsd.sh
Run jps to ensure that the ATSD java process is not running.
jps
Delete the old ATSD executable JAR file from the ATSD bin directory.
rm -v /path/to/atsd/atsd/bin/atsd*.jar
Copy the latest ATSD executable JAR file to the ATSD bin directory.
cp -v atsd/atsd/bin/atsd.$REVISION.jar /path/to/atsd/atsd/bin/
Start ATSD.
/path/to/atsd/atsd/bin/start-atsd.sh
Log in to the ATSD web interface.
Open the Settings > System Information page and verify that the co-processor file is compatible with the ATSD version.

Troubleshooting
Port Access
Ensure that the Security Group associated with the EC2 instance where ATSD is running allows access to the ATSD listening ports.
If necessary, add security group rules to open inbound access to ports 8081, 8082/udp, 8084, 8088, 8443 or 9081, 9082/udp, 9084, 9088, 9443 respectively.
Shutdown
ATSD requires a license file when connected to an HBase cluster.
Open the Settings > License page and generate a license request. Provide the license key to Axibase support.
Once the license file is signed by Axibase, start ATSD, open the Settings > License page and import the license.
./atsd/atsd/bin/start-atsd.sh
Incompatible HBase Version
If ATSD is not compatible with the HBase instance, the following error is reported when ATSD is started.
2018-09-17 14:59:08,322 ERROR [RpcServer.default.FPBQ.Fifo.handler=29,queue=2,port=16000] master.MasterRpcServices: $FileDescriptor.internalBuildGeneratedFileFrom(Descriptors.java:301)
at com.axibase.tsd.hbase.coprocessor.autogenerated.DeleteProtocol.<clinit>(DeleteProtocol.java:1584)
Check HBase version and ensure that it's 1.2.x.
echo "status" | hbase shell
DNS Resolution
In case of UnknownHostException at startup, ensure that HMaster and HRegion servers are resolvable from the ATSD server.
Caused by: java.net.UnknownHostException: ip-10-204-21-10.example.com
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.AbstractRpcClient$BlockingRpcChannelImplementation.<init>(AbstractRpcClient.java:315)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.AbstractRpcClient.createBlockingRpcChannel(AbstractRpcClient.java:267)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation.getClient(ConnectionManager.java:1639)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ScannerCallable.prepare(ScannerCallable.java:163)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ScannerCallableWithReplicas$RetryingRPC.prepare(ScannerCallableWithReplicas.java:376)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.RpcRetryingCaller.callWithRetries(RpcRetryingCaller.java:134)
Missing ATSD Coprocessor File
com.axibase.tsd.hbase.SchemaBean;Set path to coprocessor: table 'atsd_d', coprocessor com.axibase.tsd.hbase.coprocessor.CompactEndpoint, path to jar s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
com.axibase.tsd.hbase.SchemaBean;Set path to coprocessor: table 'atsd_d', coprocessor com.axibase.tsd.hbase.coprocessor.DeleteDataEndpoint, path to jar s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
...
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'series.batch.size' defined in URL
[jar:file:/mnt/atsd/atsd/bin/atsd.17245.jar!/applicationContext-properties.xml]:
Cannot resolve reference to bean 'seriesPollerHolder' while setting bean property 'updateAction';
nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'seriesPollerHolder': Injection of resource dependencies failed;
nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'serverOptionDaoImpl': Injection of resource dependencies failed;
nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'schemaBean': Invocation of init method failed;
nested exception is org.apache.hadoop.hbase.DoNotRetryIOException: org.apache.hadoop.hbase.DoNotRetryIOException:
No such file or directory: 'hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar'
Set hbase.table.sanity.checks to false at conf or table descriptor if you want to bypass sanity checks
Check the coprocessors.jar setting.
cat atsd/atsd/conf/server.properties
Sample setting:
coprocessors.jar=s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
Check that the file is present in S3.
aws s3 ls --summarize --human-readable --recursive s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib
2018-08-31 21:43:24 555.1 KiB hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
Total Objects: 1
Total Size: 555.1 KiB
If necessary, copy or replace the file.
aws s3 cp atsd/atsd-hbase.*.jar s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
Restart the HBase cluster: both HMaster and Region Servers.
Restart ATSD.
Incorrect Path to ATSD Coprocessor File
com.axibase.tsd.hbase.SchemaBean;Path to jar file for coprocessor com.axibase.tsd.hbase.coprocessor.DeleteDataEndpoint
of table atsd_d is modified to s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
com.axibase.tsd.hbase.SchemaBean;Table description should be modified. Disabling table atsd_d
org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HBaseAdmin;Started disable of atsd_d
com.axibase.tsd.hbase.SchemaBean;Error while updating schema, check hbase configuration
org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableNotEnabledException: atsd_d
Check coprocessors.jar setting in the server.properties file.
cat atsd/atsd/conf/server.properties
Verify that the coprocessors.jar is correctly set.
coprocessors.jar=s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
Check that the file is present in S3.
aws s3 ls --summarize --human-readable --recursive s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib
Sample server.properties file:
#
# HBase settings
#
hbase.compression.type = gz
hbase.table.prefix=atsd_
messages.timeToLive=31536000
#
# Network Settings
#
input.port = 9081
udp.input.port = 9082
pickle.port = 9084
http.port = 9088
https.port=9443
https.keyStorePassword=****
https.keyManagerPassword=****
https.trustStorePassword=
coprocessors.jar=s3://atsd/hbase-root/lib/atsd-hbase.jar
Restart the HBase cluster: both HMaster and Region Servers.
Restart ATSD.
