SQL Scheduled Store
Overview
The Store option for scheduled SQL queries can be used to write the results of a query back into the database as derived series.
Use Cases
- Create derived series that are frequently accessed but require expensive processing and calculation from the underlying data.
- Create cleansed series by discarding invalid values and interpolating sample values in missing interval gaps.
- Create normalized series by replacing synonyms, for example by storing data for
tag.country=Chinaandtag.country=Republic of Chinain one derived series. - Store temporal aggregations for long-term retention based on detailed data that is subject to pruning after a certain expiration date.
- Implement multi-stage data processing that cannot be programmed using the existing SQL syntax, for example, nested aggregations
AVG(SUM(value))or moving averages.
Mapping
Each row in the result set is converted into one or multiple derived series based on column names and data types.
entity, datetime, and tag columns are mapped based on names.
The remaining numeric columns are classified as metric name columns.
SELECT datetime,
'DC-1' AS "entity",
AVG(value) AS "temp_daily_avg",
PERCENTILE(90, value) AS "temp_daily_perc_90"
-- mapped to datetime, entity, for metric with name = temp_daily_avg and for metric with name = temp_daily_perc_90
FROM temperature
WHERE datetime >= CURRENT_MONTH
GROUP BY PERIOD(1 DAY)
Rows containing multiple numeric columns produce a corresponding number of series commands.
| datetime | entity | temp_daily_avg | temp_daily_perc_90 |
|----------------------|--------|----------------|--------------------|
| 2017-08-01T00:00:00Z | DC-1 | 21.01 | 27.17 |
| 2017-08-02T00:00:00Z | DC-1 | 22.20 | 28.24 |
The result set is converted into series commands and stored in the database:
series e:dc-1 d:2017-08-01T00:00:00Z m:temp_daily_avg=21.01 m:temp_daily_perc_90=27.17
series e:dc-1 d:2017-08-02T00:00:00Z m:temp_daily_avg=22.20 m:temp_daily_perc_90=28.24
Column Requirements
The columns are mapped to command fields based on column name and data type. Column aliases can be defined to ensure that the query results meet the following requirements:
Required Columns
| Name | Data Type | Occurrence | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
datetime | string | 0-1 | The date of the record in ISO format (1). |
time | long | 0-1 | The date of the record in Unix time with millisecond precision (1). |
entity | string | 1 | Name of the entity under which the new series is stored. |
- any - | numeric | 1-* | Metric name for the stored series (2). |
- (1) Only one of the date columns,
datetimeortime, must be included in the results. - (2) The column is classified as a
metricif it has a numeric datatype and does not match the rules applicable to other column types.
Optional Series Tag Columns
| Name | Data Type | Occurrence | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
tags.{name} | string | 0-* | Series tag for the stored series. Tag name set by discarding tags. prefix.Cell value contains tag value. |
tags | string | 0-* | Series tags for the stored series, encoded as key=value pairs separated by semi-colon.Cell value contains tag names and values. |
Optional Metadata Tag Columns
| Name | Data Type | Occurrence | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
metric.tags.{name} | string | 0-* | Metric tag for each metric in the row. Tag name set by discarding metric.tags. prefix.Cell value contains metric tag value. |
metric.tags | string | 0-* | Metric tags for each metric in the row, encoded as key=value separated by semi-colon. Cell value contains metric tag names and values. |
entity.tags.{name} | string | 0-* | Entity tag for the entity in the row. Tag name set by discarding entity.tags. prefix.Cell value contains entity tag value. |
entity.tags | string | 0-* | Entity tags for the entity in the row, encoded as key=value separated by semi-colon. Cell value contains entity tag names and values. |
Optional Metadata Field Columns
| Name | Data Type | Occurrence | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
metric.{field-name} | string | 0-* | Metric field for each metric in the row. Field name set by discarding metric. prefix.Cell value contains metric field value. |
entity.{field-name} | string | 0-* | Entity field for the entity in the row. Field name set by discarding entity. prefix.Cell value contains entity field value. |
- The following metadata fields are read-only and cannot be set:
metric.name,metric.lastInsertTime,entity. groups.
Table Names
The table prefix included in the fully qualified column names is ignored when classifying the columns.
The name of the column is resolved as entity in both cases below:
SELECT t1.entity ... FROM "my-table" t1
SELECT entity ... FROM "my-table"
Metadata Commands
Columns starting with 'entity.tags.', 'metric.tags.', or 'metric.{field-name}' prefixes generate entity and metric metadata commands.
SELECT datetime,
'dc-1' AS "entity",
'SVL' as "entity.tags.location",
'Celcius' AS "metric.units",
AVG(value) AS "temp_daily_avg"
-- mapped to datetime, entity, entity.tag with name = location, metric field units, for metric with name = temp_daily_avg
FROM temperature
WHERE datetime >= CURRENT_MONTH
GROUP BY PERIOD(1 DAY)
| datetime | entity | entity.tags.location | metric.units | temp_daily_perc_90 |
|----------------------|--------|----------------------|--------------|--------------------|
| 2017-08-01T00:00:00Z | DC-1 | SVL | Celcius | 27.17 |
| 2017-08-02T00:00:00Z | DC-1 | SVL | Celcius | 28.24 |
Produced commands:
entity e:dc-1 t:location=SVL
metric m:temperature_daily_perc_90 u:Celcius
series e:dc-1 d:2017-08-01T00:00:00Z m:temp_daily_perc_90=27.17
series e:dc-1 d:2017-08-02T00:00:00Z m:temp_daily_perc_90=28.24
Duplicates
Since a query can create series commands for existing dates, the Check Last Time option provides a way to control how duplicates are handled.
If Check Last Time is enabled, the series command is inserted if its timestamp is greater than the timestamp of the previously stored values for the given series key.
Validation
To test that a query complies with all requirements, execute the query in the SQL Console and click Store.
Click Test to review the produced commands and resolve any errors.
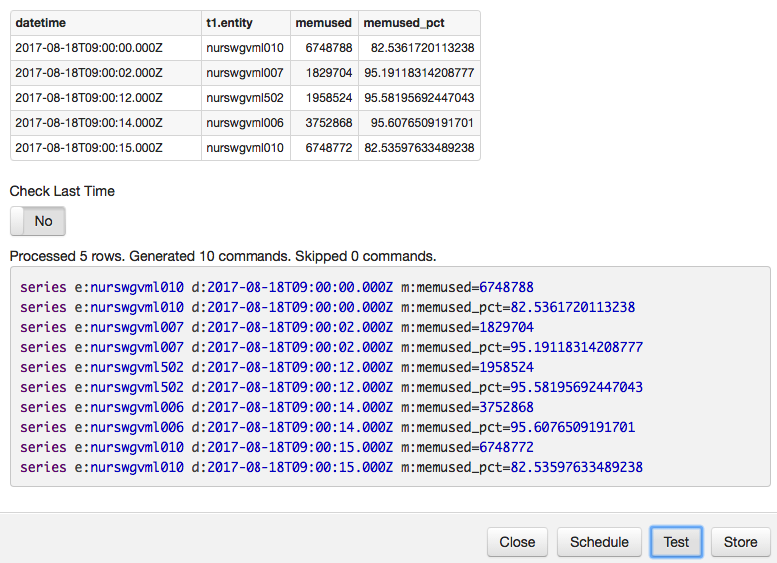
Click Store to load the new derived series in the database.
Click Schedule to created a scheduled SQL job to create and store new records for derived series continuously.
Monitoring
The results of scheduled SQL jobs with the Store option can be monitored by processing messages with type=Application, source=atsd_export and report_type=sql.
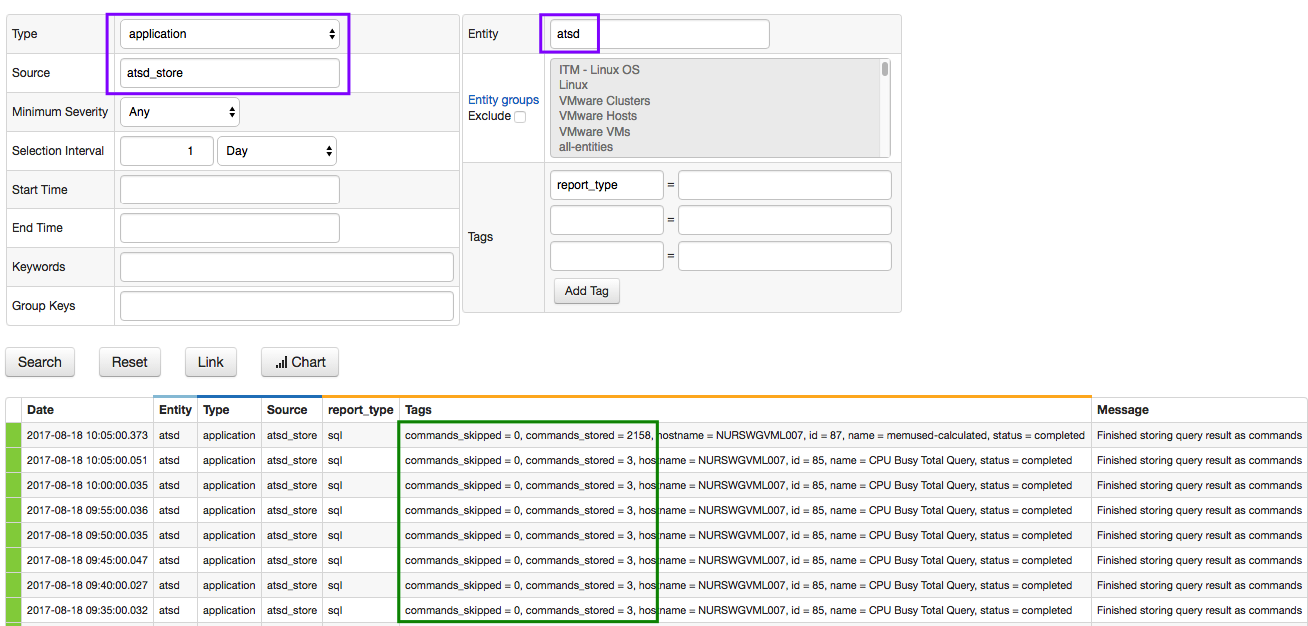
Examples
Summarizing Expiring Data
Scheduled SQL queries with Store option can be used to calculate and retain statistical averages from expiring detailed data.
Schedule such queries to execute before the raw data is deleted.
In the example below, the query runs every night (at 00:15) to calculate hourly average and maximum for each series in the underlying metrics.
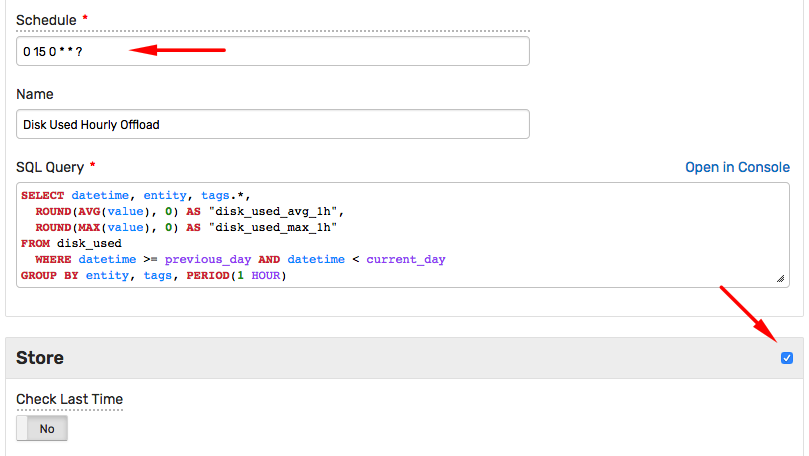
The derived metrics are then stored under new names. You can adopt a naming convention for derived metrics such as {metric}_{function}_{period}.
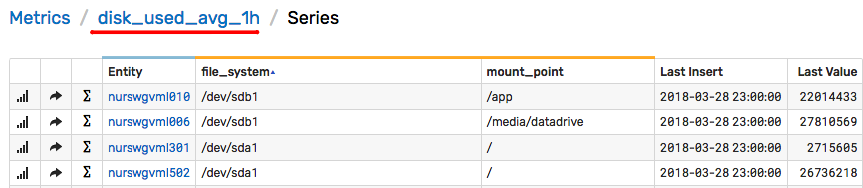
SELECT datetime, entity, tags.*,
-- specify derived metric names, for example {metric}_{function}_{period}
ROUND(AVG(value), 0) AS "disk_used_avg_1h",
ROUND(MAX(value), 0) AS "disk_used_max_1h"
-- specify metric with raw data to summarize
FROM disk_used
WHERE datetime >= previous_day AND datetime < current_day
-- choose summarization period, such as 1-hour
GROUP BY entity, tags, PERIOD(1 HOUR)
