User Authentication
Authentication mechanisms implemented in ATSD control how users present and verify their identity when accessing protected resources such as web pages or API endpoints.
Supported authentication mechanisms:
- Form Authentication
- Basic Authentication
- Token Authentication
Authentication Mechanisms
Form Authentication
Accessing the web interface requires the user to provide the correct username and password on the login page.

The user is granted access if the account for the specified username exists, the password is correct, and the account is not locked or expired.
When activated, the Remember Me option on the login form stores the submitted username in the user's browser cache.
Basic Authentication
An HTTP request to an API URL starting with /api/ is required to include an Authorization header with type Basic. See examples below.
If the Authorization header is missing, the client is prompted to provide username and password.
Once credentials are verified, subsequent API requests within the same session can be executed without the Authorization header.
This type of authentication is suited for client programs that need to perform a wide array of API requests.
curl https://atsd_hostname:8443/api/v1/series/query \
--insecure \
--user {username}:{password} \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '[{"metric":"mpstat.cpu_busy", "entity":"nurswgvml007", "startDate":"previous_day", "endDate": "now"}]' > response.json
Requests authenticated with Basic Authentication are subject to the same permission checks as the underlying user account.
Token Authentication
An HTTP request to a specific API URL starting with /api/ can be authenticated by including the Authorization header with type Bearer.
--header "Authorization: Bearer <API-TOKEN>"
Passing the token in the URL is not supported because of the security weaknesses.
The token allows access to a specific URL, consisting of path and query parameters. The URL and the HTTP method are fixed at the time the token is created. The order of query parameters and the URL-encoding scheme is not important.
To allow access to a variable URL with placeholders, where parameter value or path parts can be substituted at request time, use the <> syntax.
/api/v1/portal/export?id=<>
Allows:
- /api/v1/portal/export?id=1
- /api/v1/portal/export?id=2
- /api/v1/portal/export?id=abc
/api/v1/csv/<>
Allows:
- /api/v1/csv/export
- /api/v1/csv/import
Users can issue and revoke tokens on the Account Settings page. The tokens can be set to automatically expire and be subject to IP address restrictions.
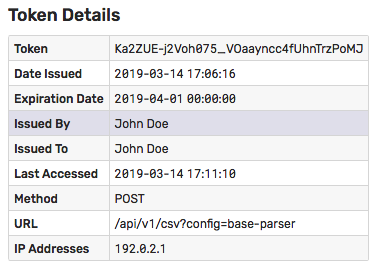
Token authentication does not require sharing username and password with client programs and is suited for automation scripts that need to execute a limited set of actions such as uploading a CSV file.
curl https://atsd_hostname:8443/api/v1/csv?config=base-parser \
--insecure --request POST \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <API-TOKEN>" \
--header "Content-Type: text/csv" \
--form "data=@daily.csv"
IP address restrictions set for the token override any IP address restrictions set for the underlying user account.
Requests authenticated with Token Authentication are subject to the same permission checks as the underlying user account.
User Account Types
User accounts are stored in the database.
The user account can be configured to use either Local or LDAP authentication.
Local Accounts
When using Local authentication, the database stores the hashcode of the user password in the underlying HBase database.
The user identity is verified if the hashcode of the submitted password matches the stored hashcode for the specified username.
The password is subject to the requirements outlined below.
LDAP Accounts
When using LDAP authentication, the database verifies that the account exists in the database and the password is confirmed by submitting an authentication request to the remote LDAP server.
If the LDAP server locates the specified account and confirms its password, the user is allowed to access the database.
The access is denied if the LDAP server cannot find the account or if the LDAP account is locked, disabled, or requires password change.
Password Requirements
The following password rules apply to Local accounts:
Password must contain at least six (
6) characters by default.Adjust the default minimum length in the
server.propertiesfile with theuser.password.min.lengthsetting.Passwords are case-sensitive.
Password can contain the following characters:
Any Unicode character categorized as an alphanumeric character.
Special characters:
~ ! @ # $ % ^ & * _ - + = ` | \ ( ) { } [ ] : ; ” ‘ < > , . ? / " '
Built-in Account
- When accessed for the first time after installation, the database presents a configuration web page for the default administrator account. This account is granted an
ADMINrole withAll Entities: ReadandAll Entities: Writepermissions.
Changing Password
Users with Local accounts can modify their password by clicking on the user icon in the top menu.
Users are not allowed to change their own type, roles, group membership, or entity permissions.
Resetting Password
User passwords for Local accounts are stored as hashcodes. As a result, recovering a lost password is not supported.
To reset the password for a user account:
- Open the
server.propertiesfile. - Add
user.password.reset.username={username}anduser.password.reset.password={new-password}settings and save the file.- Restart the database.
- Remove the above settings from the
server.propertiesfile to prevent password resets on subsequent restarts.
- Open the
If the account being reset is configured as LDAP type, the type is changed to Local.
Guest Access to Data API
To enable anonymous access to Data API query methods, set api.guest.access.enabled=true in the server.properties file and restart the database.
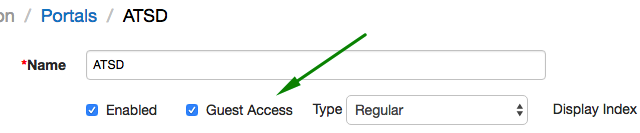
Guest Access to Portals
To expose the portal to non-authenticated visitors, open the Portals tab in the top menu, click Configure, open the portal editor and check Guest Access.
Since charts displayed in the portals are loaded via Data API, the Guest Access option is available only when Data API is configured for anonymous access.
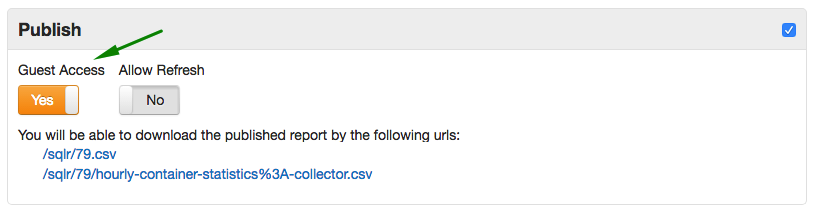
Guest Access to SQL Reports
To make SQL query results visible to non-authenticated visitors, check Guest Access on the query configuration page.
Note
Guest access to Data API is not required in this case.
HTTP Basic Authorization Examples
- Java Example:
URL url = new URL("http://192.0.2.6:8088/api/v1/series");
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setRequestProperty("charset", "utf-8");
String authString = userName + ":" + password;
String authEncoded = DatatypeConverter.printBase64Binary(authString.getBytes());
conn.setRequestProperty("Authorization", "Basic " + authEncoded);
curlExample:
curl https://atsd_hostname:8443/api/v1/properties/query \
--insecure --user {username}:{password} \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '[{"type":"disk","entity":"nurswgvml007","startDate":"2016-05-25T04:00:00Z","endDate":"now"}]'
Authentication and Authorization Errors
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
01 | General Server Error |
02 | Username Not Found |
03 | Bad Credentials |
04 | Disabled LDAP Service |
05 | Corrupted Configuration |
06 | MS Active Directory |
07 | Account Disabled |
08 | Account Expired |
09 | Account Locked |
10 | Logon Not Permitted At Time |
11 | Logon Not Permitted At Workstation |
12 | Password Expired |
13 | Password Reset Required |
14 | Wrong IP Address |
15 | Access Denied |
16 | Authorization Token Expired |
