Selecting Series
Reference
- Database Schema
- Exploring Series
- Selecting Specific Series
- Selecting Multiple Series with Tags
- Merging Series
- Selecting Series for Multiple Entities
- Retrieving Series from the Database
- Controlling Displayed Series
Database Schema
Widget configuration syntax provides a way to load and display time series data stored in a database. As series values change over time, their history can be visualized on portals with various widgets.
[widget]
type = chart
# widget settings
[series]
# series 1 settings
[series]
# series 2 settings
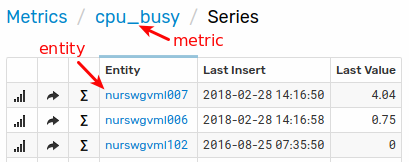
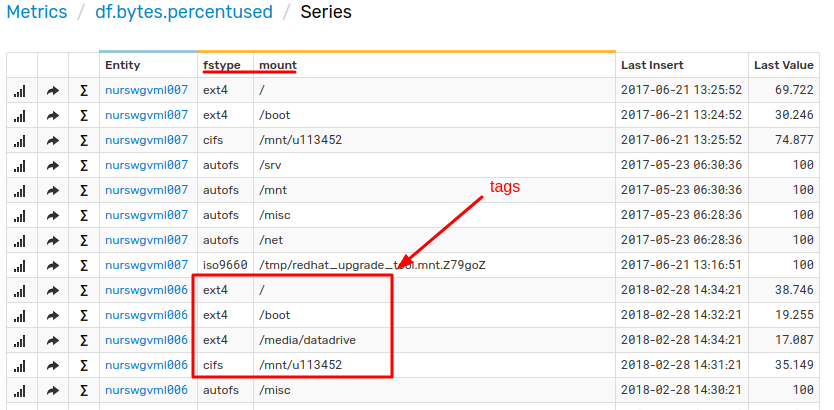
Each series is identified by a composite key which consists of a metric, entity, and optional name/value pairs called series tags.
[series]
metric = cpu_busy
entity = nurswgvml007
[series]
metric = df.bytes.percentused
entity = nurswgvml006
[tags]
mount = /
fstype = ext4
- An entity is a physical or logical object such as
nurswgvml007(hostname) orbr-1705(equipment). - A metric represents the name of a measurable numeric attribute such as
cpu_busyortemperature. - Series tags provide an additional level of detail for measurements such as a disk mount point or process Id. The series tags are optional.
An entity can be instrumented and monitored with multiple metrics, just as the same metric can be collected for multiple entities.
Exploring Series
Search available series from the Series tab in the main menu.
Alternatively, for known entities, explore metrics and series via portals containing drop-down list selectors.
Selecting Specific Series
To display values for a specific series, specify the exact series key at the configuration [series] level:
# Series without Tags
metric = cpu_busy
entity = nurswgvml007
# Series with Tags
metric = df.bytes.percentused
entity = nurswgvml006
[tags]
mount = /
fstype = ext4
Selecting Multiple Series with Tags
By default, the database returns all series matching the request, including series with additional tags not enumerated in the request.
This enables loading series using only a subset of tags that are still sufficient to uniquely identify the series:
# Series with Tags
metric = df.bytes.percentused
entity = nurswgvml006
[tags]
mount = /
The above configuration matches all series with mount=/ tag, including series that have other tags.
To disable partial tag match, use the exact-match = true | false setting:
# Series with Tags
metric = df.bytes.percentused
entity = nurswgvml006
exact-match = true
[tags]
mount = /
When partial match is disabled, ATSD returns series with exactly the same combination of tags as specified in the request.
Each series request in the configuration can match multiple series. To control how multiple matching series are processed, use the merge-series setting.
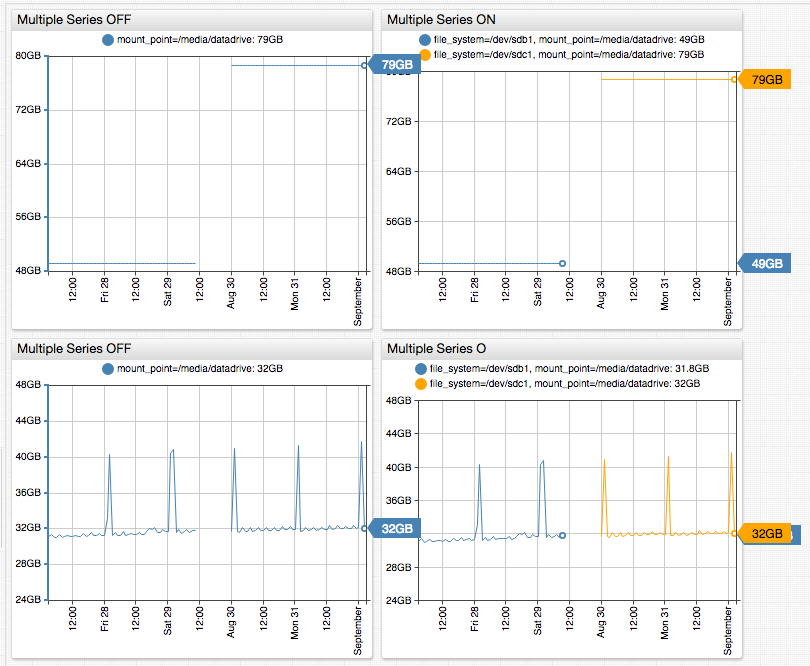
Merging Series
Joining multiple series with different tags into one series is useful when certain tags can be ignored.
date metric entity tags value
2018-06-15 00:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/,fstype=ext3 10.2 <- series-1
2018-06-15 01:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/,fstype=ext3 10.3 <- series-1
2018-06-15 02:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/,fstype=ext4 10.1 <- series-2
2018-06-15 03:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/,fstype=ext4 10.2 <- series-2
In the previous example, the underlying series do not overlap and can be merged without duplication.
date metric entity tags value
2018-06-15 00:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/ 10.2 <- series-3
2018-06-15 01:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/ 10.3 <- series-3
2018-06-15 02:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/ 10.1 <- series-3
2018-06-15 03:00:00 df.bytes.percentused nurswgvml006 mount=/ 10.2 <- series-3
Examples:
/media/datadrivefile system re-mounted on a larger disk without change to mount point.- Containers with different identifiers launched on schedule to perform identically named daily tasks.
- Measurements recorded for scientific experiments and tags contain experiment ID and input parameters.
Selecting Series for Multiple Entities
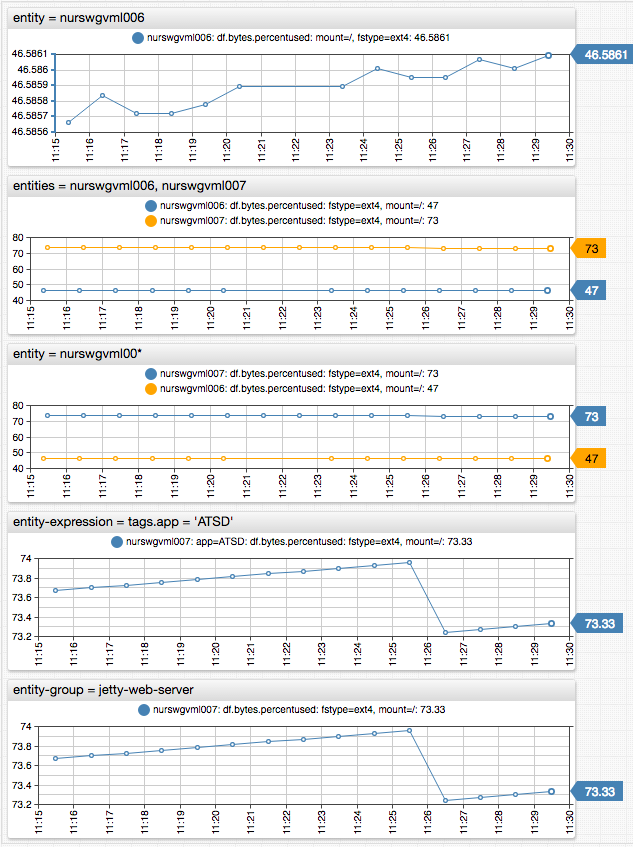
[widget] syntax provides a number of options to select series for multiple entities with same metric:
# Select specific entity by name
entity = nurswgvml006
# Select multiple entities by name using ? and * wildcards
entity = nurswgvml*
# Select all entities
entity = *
# Select an array of entities by name
entities = nurswgvml006, nurswgvml007
# Select an array of entities by name or pattern
entities = nurswgvml111, nurswgvml00*
# Select entities matching an expression referencing name, label, entity tags, properties
entity-expression = tags.app = 'ATSD'
# Select entities belonging to the specified entity group
entity-group = nur-collectors
Refer to the Data API Documentation for details on entity filters.
# Retrieve series for entities starting with nurswgvml00
[series]
entity = nurswgvml00*
[tags]
mount = /
fstype = ext4
Retrieving Series from the Database
As an alternative to defining a [series] manually or using wildcards, widget syntax supports the getSeries() and getTags() functions to retrieve series lists from the server.
getTags() function:
var tags = getTags('df.bytes.percentused', 'mount', 'nurswgvml006')
for tagValue in tags
[series]
[tags]
mount = @{tagValue}
endfor
getSeries() function:
var seriesList = getSeries('df.bytes.percentused', 'nurswgvml006')
for sobj in seriesList
[series]
[tags]
for tagName in Object.keys(sobj.tags)
"@{tagName}" = @{sobj.tags[tagName]}
endfor
endfor
Controlling Displayed Series
The series-limit setting limits the number of possible series returned by the database for wildcard queries.
Because the limit is applied to matched series before sorting, results can vary between requests which makes the setting
helpful when exploring a dataset by preventing a widget from loading excessive series into browser memory.
entity = *
series-limit = 10
[series]
[tags]
fstype = ext4
To control which series are displayed, use the display and enabled filter settings which are evaluated on the client.
entity = *
display = value == top(1) || value == bottom(1)
[series]
[tags]
fstype = ext4
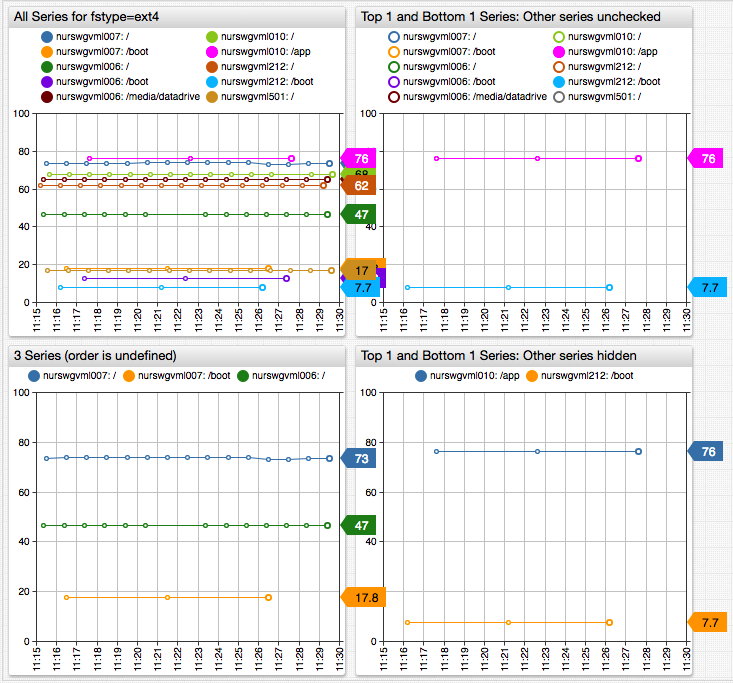
Additionally, the limit setting reduces the number of samples displayed for each series. This makes queries
execute faster when loading data for high-frequency series from the server, in particular during design and validation stages.
