SNMP Job
The SNMP job collects metrics from IP-addressable devices over the SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) protocol. The job monitors system availability and performance without installing a custom agent on the target system. The statistics are exposed by a SNMP daemon available by default on network devices and as a package for Linux, Windows, and HP-UX operating systems.
Prerequisites
- Install
snmppackage on the Collector server.
apt-get install snmp
yum -y install net-snmp net-snmp-utils
- Verify that
snmptranslate -hutility is installed.
USAGE: snmptranslate [OPTIONS] OID [OID]...
Version: 5.7.2
...
Quick Start
- Import MIB files into Collector as described in the Base MIB files section.
- Import
snmp-osSNMP Job into Collector. - Open the Collections > Item Lists page in Collector, specify monitored hosts in the
SNMP Deviceslist. - Open the
snmp-osjob in Collector, open thesystem statisticsconfiguration and click Test to check connectivity. Run the job manually to collect initial metric values. - Log in to ATSD and verify that SNMP metrics are displayed on the Metrics tab with the
snmp*prefix. - Import
group-snmpSNMP entity group into ATSD. - Import
portal-snmpSNMP Portal into ATSD. See an example portal below.
Job Settings
The SNMP job allows creating multiple configurations to query objects in different MIB files. The configurations are executed sequentially, while SNMP GETBULK operations to remote devices in each configuration are executed in parallel.
Each configuration retrieves pre-defined object values, identified by OID (Object Identifier), from hostnames or IP addresses in the Device List. Metrics collected from the same device are sent into ATSD under an entity name based on the device hostname or IP address as specified in the Device List.
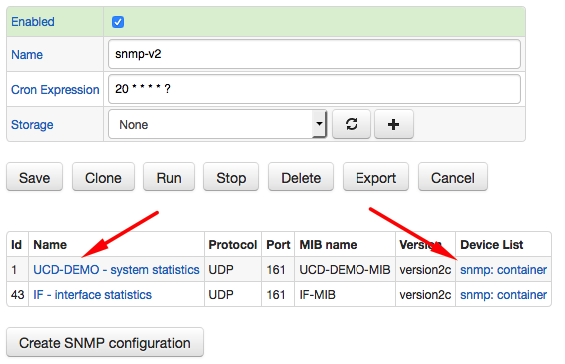
Configuration Settings
The settings specify the list of devices to query as well as connection properties.
Query Settings
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Device List | List of hostnames or IP addresses to query. |
| Metric Prefix | Prefix added to metric names sent into ATSD. |
| MIB Name | MIB file containing object definitions. |
| Metric OIDs | Object names containing numeric metric values. |
| Series Tag OIDs | Object names containing series tags. |
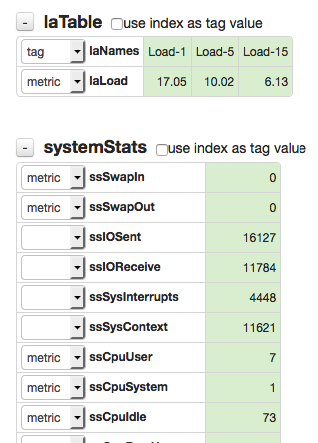
To populate the list of collected metric objects, click Configure button to view the editor.
Enter a hostname or IP address for one of the target systems and click Load All Values. Choose which objects to collect. If the object has an additional dimension such as interface or disk name, classify such OID as tag.
Connection Settings
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Transport | TCP or UDP protocol used for connecting to the devices. |
| Port | TCP or UDP port. |
| Version | SNMP protocol version. |
| Community | SNMP community name, such as public. |
| Timeout, seconds | Number of seconds after which Collector interrupts the query. 0 or -1 is unlimited. |
| Retries | Number of connection retries in case of network failure. |
| Maximum Repetitions | Maximum number of iterations over the repeating variables. |
| Non Repeaters | Number of supplied variables that must not be iterated over. |
Supported SNMP protocol versions:
- SNMP
v2c - SNMP
v3
Security Settings
The following settings apply to SNMP protocol v3.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication Protocol | Encryption protocol for authentication. Allowed values: MD5, SHA. |
| Security Name | Username. |
| Authentication Pass Phrase | Password. |
| Privacy Pass Phrase | Pass phrase for data transmission. |
| Privacy Protocol | Data encryption protocol. Allowed values: DES, TRIPLE_DES, AES128, AES192, AES256. |
| Security Level | Allowed values:NO_AUTH_NO_PRIV: no authentication, no encryption. AUTH_NO_PRIV: authentication, no encryption. AUTH_PRIV: authentication and encryption. |
Testing Connections
Network connectivity between Collector and a remote system is required.
To check that the SNMP daemon on the target device is reachable, open the SNMP configuration page.
Select a MIB file in the drop-down list.
Fill out connection properties and click Configure. The configuration settings are saved automatically, when the configuration editor is launched.
Enter the target hostname or IP address and click Load All Values.
Configuration Example
SNMP configuration example:
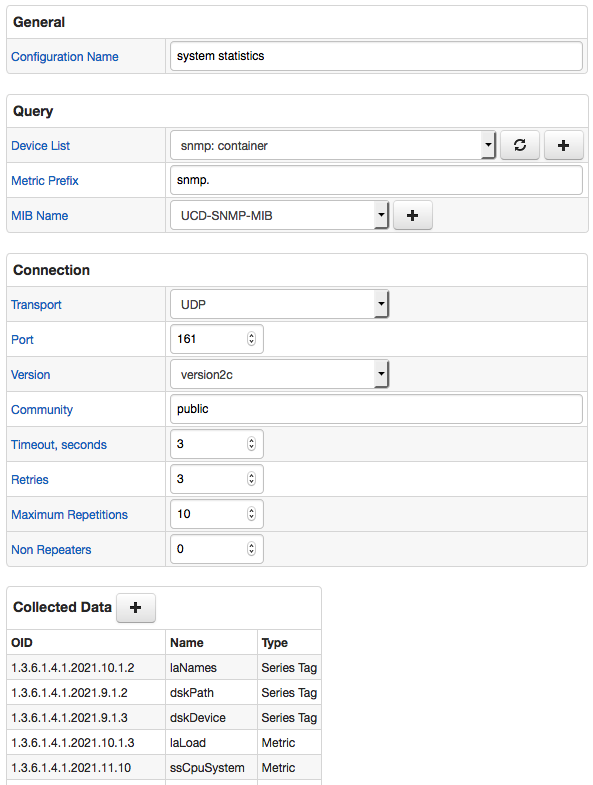
Click Test to view sample series commands for the given configuration.
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.laLoad=1.56 t:laNames=Load-1
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.laLoad=2.14 t:laNames=Load-15
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.laLoad=1.97 t:laNames=Load-5
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memShared=494356
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memBuffer=403904
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memTotalReal=65124968
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memAvailReal=16156972
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memCached=25270224
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memTotalFree=49637572
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memAvailSwap=33480600
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T11:14:56.481Z m:snmp.memTotalSwap=33537916
MIB Files
The SNMP daemon running on the remote system publishes available configuration and performance objects using OIDs (object identifiers). The OIDs are defined in Management Information Base (MIB) files and contain information such as object name, type, data type etc.
laLoad .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3
enterprises.ucdavis.laTable.laEntry.laLoad
laLoad OBJECT-TYPE
-- FROM UCD-SNMP-MIB
-- TEXTUAL CONVENTION DisplayString
SYNTAX OCTET STRING (0..255)
DISPLAY-HINT "255a"
MAX-ACCESS read-only
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION "The 1,5 and 15 minute load averages (one per row)."
::= { iso(1) org(3) dod(6) internet(1) private(4) enterprises(1) ucdavis(2021) laTable(10) laEntry(1) 3 }
Collector needs access to MIB files to translate OIDs received from the remote systems into object names used in ATSD the metric and series tag names.
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3 --> laLoad
series e:192.0.2.1 d:2018-06-27T10:09:19.649Z t:laNames=Load-1 m:snmp.laLoad=2.79
The SNMP job supports built-in and custom MIB files.
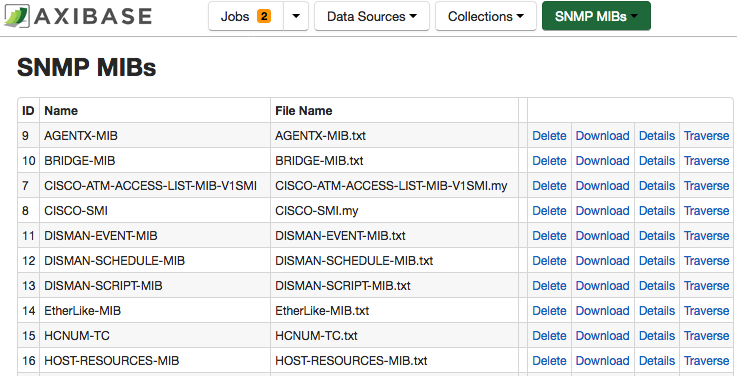
SNMP MIB Import
Load MIB files into the Collector instance on the Admin > SNMP MIBs page.
Perform this task initially, as part of post-installation configuration, as well as when you enable monitoring for a new class of remote systems with custom MIB files.
Open Admin > SNMP MIBs > Upload MIB page.
Attach a MIB file and click Upload.
The MIB file is validated and translated using the snmptranslate utility installed on the underlying Linux operating system. A translated list of OIDs is loaded into the Collector database.
MIB Tree
MIB format is hierarchical and allows for inheriting definitions from parent MIBs. As a result, you must import parent MIBs first.
IF-MIB DEFINITIONS ::= BEGIN
IMPORTS
MODULE-IDENTITY, OBJECT-TYPE, Counter32, Gauge32, Counter64,
Integer32, TimeTicks, mib-2,
NOTIFICATION-TYPE FROM SNMPv2-SMI
TEXTUAL-CONVENTION, DisplayString,
PhysAddress, TruthValue, RowStatus,
TimeStamp, AutonomousType, TestAndIncr FROM SNMPv2-TC
MODULE-COMPLIANCE, OBJECT-GROUP,
NOTIFICATION-GROUP FROM SNMPv2-CONF
snmpTraps FROM SNMPv2-MIB
IANAifType FROM IANAifType-MIB;
When you import the MIB file Collector searches for any parent files, specified in the IMPORTS section, among the previously loaded MIB files as well as MIB files stored on the underlying operating system.
System MIB directory location:
- On Linux, the MIB files are stored in the
/usr/share/snmpdirectory. - On HP-UX, the MIB files are stored in the
/var/opt/OV/share/snmp_mibsdirectory.
Base MIB Files
The following table contains links to MIB files for monitoring operating system performance metrics. Upload the MIB files into your Collector instance in the order specified in the Priority column.
| Priority | MIB | Description | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SNMPv2-SMI | - | - |
| 2 | SNMPv2-TC | Represents textual information taken from the NVT ASCII character set | SNMPv2-SMI |
| 3 | SNMPv2-MIB | The MIB module for SNMP entities | SNMPv2-TC |
| 4 | UCD-SNMP-MIB | System load average, CPU utilization, memory configuration and usage, disk used. | SNMPv2-MIB |
| 5 | IF-MIB | Network interface counters | SNMPv2-MIB |
SNMP Portal
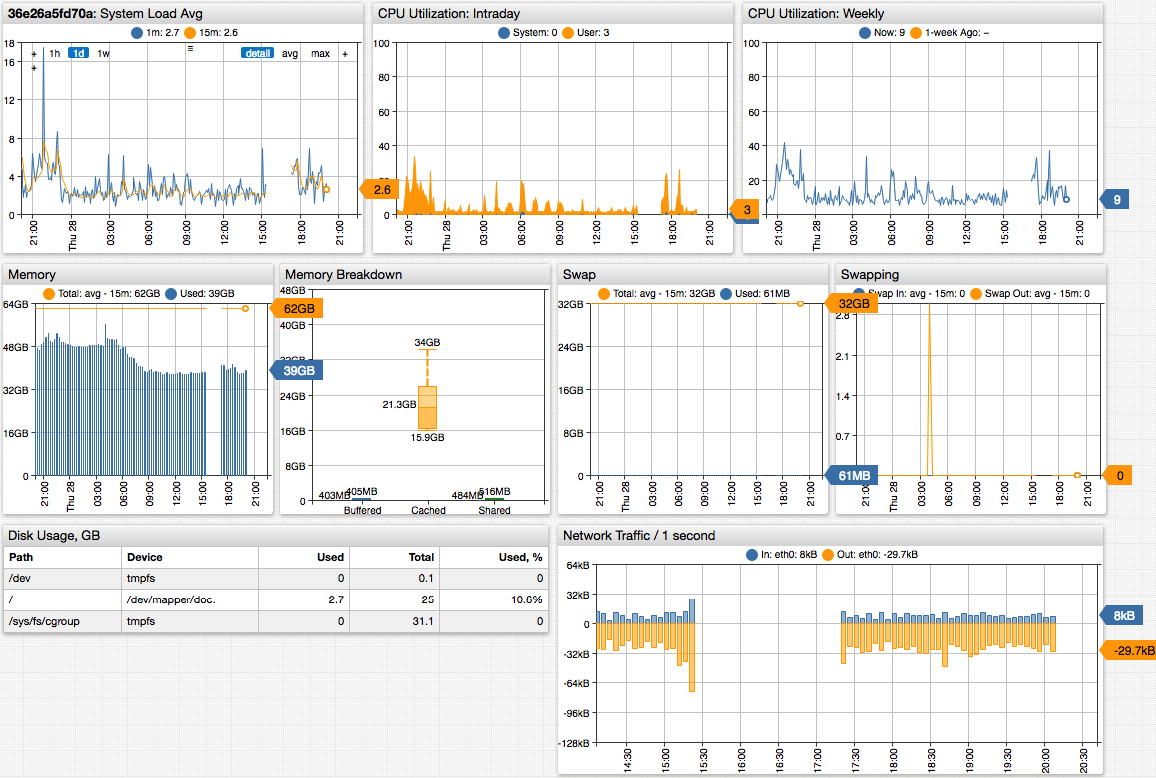
Troubleshooting
Connectivity
Test that the target server is accessible using snmpwalk utility.
snmpwalk -v2c -c public udp:192.0.2.1:161
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: "Linux NURSWGVML007 4.4.0-127-generic #153-Ubuntu SMP Sat May 19 10:58:46 UTC 2018 x86_64"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 = OID: iso.3.6.1.4.1.8072.3.2.10
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (15651) 0:02:36.51
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0 = STRING: "john.doe@example.org>"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: "192.0.2.1"
...
System View Restriction
On some systems, access to OIDs other than those containing basic information is disabled in by the SNMP daemon.
In case of Bad value(endOfMibView) error, modify the SNMP daemon configuration on the target server.
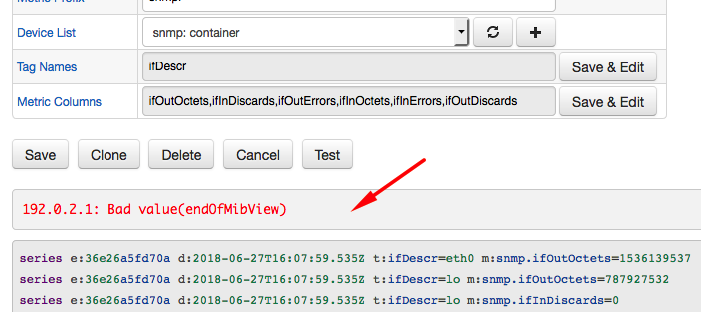
The error is displayed as end of the MIB tree at the end of the the snmpwalk output.
...
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.7.0 = No more variables left in this MIB View (It is past the end of the MIB tree)
Open the /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf file.
Ubuntu/Debian
Remove -V systemonly restriction from the rocommunity setting.
# rocommunity public default -V systemonly
rocommunity public default
Restart the SNMP daemon.
service snmpd restart
RHEL/Centos
# group context sec.model sec.level prefix read write notif
access notConfigGroup "" any noauth exact systemview none none
Create a new view named all containing all OIDs.
# name incl/excl subtree mask(optional)
view systemview included .1.3.6.1.2.1.1
view systemview included .1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.1
view all included .1
Grant the public community read-only permissions to the all view.
# group context sec.model sec.level prefix read write notif
access notConfigGroup "" any noauth exact all none none
Restart the SNMP daemon to apply the changes.
Unknown Objects
To check that the remote system publishes operating system OIDs in the UCD-SNMP-MIB MIB, execute the snmpwalk command with the OID filter set to 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021 (iso(1) org(3) dod(6) internet(1) private(4) enterprises(1) ucdavis(2021)).
snmpwalk -v2c -c public udp:192.0.2.1:161 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021
The expected output contains a list of nested OIDs.
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.1.1 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.1.2 = INTEGER: 2
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.1.3 = INTEGER: 3
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.2.1 = STRING: "mountd"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.2.2 = STRING: "ntalkd"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.2.3 = STRING: "sendmail"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.3.1 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.3.2 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.3.3 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.4.1 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.4.2 = INTEGER: 4
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.4.3 = INTEGER: 10
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.5.1 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.5.2 = INTEGER: 0
...
SNMP Object Reference
UCD-SNMP-MIB
Table
prTable:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2Object Description prEntry1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1An entry containing a process and its statistics. prIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.1Reference Index for each observed process. prNames1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.2The process name we're counting/checking on. prMin1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.3The minimum number of processes that must be running. An error setting is generated if the number of running processes is < the minimum. prMax1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.4The maximum number of processes that must be running. An error setting is generated if the number of running processes is > the maximum. prCount1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.5The number of current processes running with the name in question. prErrorFlag1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.100A Error setting to indicate trouble with a process. Setting goes to 1if there is an error,0if no error.prErrMessage1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.101An error message describing the problem (if one exists). prErrFix1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.102Setting this to one tries to fix the problem if the agent has been configured with a script to call to attempt to fix problems automatically using remote snmp operations. prErrFixCmd1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.2.1.103The command that gets run when the prErrFixcolumn is set to1.Table
memory:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4Object Description memIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.1Bogus Index. This must always return the integer 0.memErrorName1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.2Bogus Name. This must always return the string swap.memTotalSwap1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.3The total amount of swap space configured for this host. memAvailSwap1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.4The amount of swap space currently unused or available. memTotalReal1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.5The total amount of real/physical memory installed on this host. memAvailReal1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.6The amount of real/physical memory currently unused or available. memTotalSwapTXT1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.7The total amount of swap space or virtual memory allocated for text pages on this host. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not distinguish text pages from other uses of swap space or virtual memory. memAvailSwapTXT1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.8The amount of swap space or virtual memory currently being used by text pages on this host. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not distinguish text pages from other uses of swap space or virtual memory. Note that (despite the name), this value reports the amount used, rather than the amount free or available for use. For clarity, this object is being deprecated in favour of memUsedSwapTXT(16).memTotalRealTXT1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.9The total amount of real/physical memory allocated for text pages on this host. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not distinguish text pages from other uses of physical memory. memAvailRealTXT1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.10The amount of real/physical memory currently being used by text pages on this host. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not distinguish text pages from other uses of physical memory. Note that (despite the name), this value reports the amount used, rather than the amount free or available for use. For clarity, this object is being deprecated in favour of memUsedRealTXT(17).memTotalFree1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.11The total amount of memory free or available for use on this host. This value typically covers both real memory and swap space or virtual memory. memMinimumSwap1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.12The minimum amount of swap space expected to be kept free or available during normal operation of this host. If this value (as reported by memAvailSwap(4)) falls below the specified level, thenmemSwapError(100)is set to1and an error message made available viamemSwapErrorMsg(101).memShared1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.13The total amount of real or virtual memory currently allocated for use as shared memory. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not explicitly identify memory as specifically reserved for this purpose. memBuffer1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.14The total amount of real or virtual memory currently allocated for use as memory buffers. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not explicitly identify memory as specifically reserved for this purpose. memCached1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.15The total amount of real or virtual memory currently allocated for use as cached memory. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not explicitly identify memory as specifically reserved for this purpose. memUsedSwapTXT1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.16The amount of swap space or virtual memory currently being used by text pages on this host. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not distinguish text pages from other uses of swap space or virtual memory. memUsedRealTXT1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.17The amount of real/physical memory currently being used by text pages on this host. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not distinguish text pages from other uses of physical memory. memSwapError1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.100Indicates whether the amount of available swap space (as reported by memAvailSwap(4)), is less than the specified minimum (defined bymemMinimumSwap(12)).memSwapErrorMsg1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.101Describes whether the amount of available swap space (as reported by memAvailSwap(4)), is less than the specified minimum (defined bymemMinimumSwap(12)).Table
extTable:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8Object Description extEntry1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1An entry containing an extensible script/program and its output. extIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.1Reference Index for extensible scripts. Simply an integer row number. extNames1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.2A Short, one name description of the extensible command. extCommand1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.3The command line to be executed. extResult1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.100The result code (exit status) from the executed command. extOutput1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.101The first line of output of the executed command. extErrFix1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.102Setting this to one tries to fix the problem if the agent has been configured with a script to call to attempt to fix problems automatically using remote snmp operations. extErrFixCmd1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.103The command that gets run when the extErrFixcolumn is set to1.Table
dskTable:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9Object Description dskEntry1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1An entry containing a disk and its statistics. dskIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.1Integer reference number (row number) for the disk mib.dskPath1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.2Path where the disk is mounted. dskDevice1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.3Path of the device for the partition dskMinimum1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.4Minimum space required on the disk (in kBytes) before the errors are triggered. Either this or dskMinPercentis configured via the agent'ssnmpd.conffile.dskMinPercent1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.5Percentage of minimum space required on the disk before the errors are triggered. Either this or dskMinimumis configured via the agent'ssnmpd.conffile.dskTotal1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.6Total size of the disk/partition (kBytes) dskAvail1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.7Available space on the disk dskUsed1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.8Used space on the disk dskPercent1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.9Percentage of space used on disk dskPercentNode1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.10Percentage of inodes used on disk dskTotalLow1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.11Total size of the disk/partition (kBytes). Together with dskTotalHighcomposes64-bit number.dskTotalHigh1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.12Total size of the disk/partition (kBytes). Together with dskTotalLowcomposes64-bit number.dskAvailLow1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.13Available space on the disk (kBytes). Together with dskAvailHighcomposes64-bit number.dskAvailHigh1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.14Available space on the disk (kBytes). Together with dskAvailLowcomposes64-bit number.dskUsedLow1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.15Used space on the disk (kBytes). Together with dskUsedHighcomposes64-bit number.dskUsedHigh1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.16Used space on the disk (kBytes). Together with dskUsedLowcomposes64-bit number.dskErrorFlag1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.100Error setting signaling that the disk or partition is under the minimum required space configured for it. dskErrorMsg1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9.1.101A text description providing a warning and the space left on the disk. Table
laTable:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10Object Description laEntry1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1An entry containing a load average and its values. laIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.1reference index/row number for each observed loadave.laNames1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.2The list of loadavenames we're watching.laLoad1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3The 1,5and15minute load averages (one per row).laConfig1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.4The watch point for load-averages to signal an error. If the load averages rises above this value, the laErrorFlagbelow is set.laLoadInt1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.5The 1,5and15minute load averages as an integer. This is computed by taking the floating pointloadaveragevalue and multiplying by100, then converting the value to an integer.laLoadFloat1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.6The 1,5and15minute load averages as an opaquely wrapped floating point number.laErrorFlag1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.100A Error setting to indicate the load-average has crossed its threshold value defined in the snmpd.conffile. Set to1if the threshold is crossed,0otherwise.laErrMessage1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.101An error message describing the loadaverageand its surpassed watch-point value.Table
systemStats:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11Object Description ssIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.1Bogus Index. This must always return the integer 1.ssErrorName1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.2Bogus Name. This must always return the string systemStats.ssSwapIn1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.3The average amount of memory swapped in from disk, calculated over the last minute. ssSwapOut1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.4The average amount of memory swapped out to disk, calculated over the last minute. ssIOSent1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.5The average amount of data written to disk or other block device, calculated over the last minute. This object has been deprecated in favour of ssIORawSent(57), which can be used to calculate the same metric, over any specified time period.ssIOReceive1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.6The average amount of data read from disk or other block device, calculated over the last minute. This object has been deprecated in favour of ssIORawReceived(58), which can be used to calculate the same metric, over any specified time period.ssSysInterrupts1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.7The average rate of interrupts processed (including the clock) calculated over the last minute. This object has been deprecated in favour of ssRawInterrupts(59), which can be used to calculate the same metric, over any specified time period.ssSysContext1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.8The average rate of context switches, calculated over the last minute. This object has been deprecated in favour of ssRawContext(60), which can be used to calculate the same metric, over any specified time period.ssCpuUser1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.9The percentage of CPU time spent processing user-level code, calculated over the last minute. This object has been deprecated in favour of ssCpuRawUser(50), which can be used to calculate the same metric, over any specified time period.ssCpuSystem1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.10The percentage of CPU time spent processing system-level code, calculated over the last minute. This object has been deprecated in favour of ssCpuRawSystem(52), which can be used to calculate the same metric, over any specified time period.ssCpuIdle1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.11The percentage of processor time spent idle, calculated over the last minute. This object has been deprecated in favour of ssCpuRawIdle(53), which can be used to calculate the same metric, over any specified time period.ssCpuRawUser1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.50The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent processing user-level code. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors.ssCpuRawNice1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.51The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent processing reduced-priority code. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not measure this particular CPU metric. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors.ssCpuRawSystem1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.52The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent processing system-level code. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors. This object sometimes is implemented as the combination of thessCpuRawWait(54)andssCpuRawKernel(55)counters, care must be taken when summing the overall raw counters.ssCpuRawIdle1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.53The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent idle. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors.ssCpuRawWait1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.54The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent waiting for IO. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not measure this particular CPU metric. This time also is included within thessCpuRawSystem(52)counter. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors.ssCpuRawKernel1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.55The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent processing kernel-level code. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not measure this particular CPU metric. This time also is included within thessCpuRawSystem(52)counter. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors.ssCpuRawInterrupt1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.56The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent processing hardware interrupts. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not measure this particular CPU metric. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors.ssIORawSent1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.57Number of blocks sent to a block device ssIORawReceived1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.58Number of blocks received from a block device ssRawInterrupts1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.59Number of interrupts processed ssRawContexts1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.60Number of context switches ssCpuRawSoftIRQ1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.61The number of ticks(typically1/100s) spent processing software interrupts. This object is not implemented on hosts where the underlying operating system does not measure this particular CPU metric. On a multi-processor system, thessCpuRaw*counters are cumulative over all CPUs, their sum is typically N*100for N processors.ssRawSwapIn1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.62Number of blocks swapped in ssRawSwapOut1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.63Number of blocks swapped out Table
fileTable:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15Object Description fileEntry1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15.1Entry of file fileIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15.1.1Index of file fileName1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15.1.2Filename fileSize1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15.1.3Size of file (kB) fileMax1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15.1.4Limit of filesize(kB)fileErrorFlag1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15.1.100Limit exceeded setting fileErrorMsg1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.15.1.101Filesizeerror messageTable
logMatch:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16Object Description logMatchMaxEntries1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.1The maximum number of logmatchentries thissnmpddaemon can support.logMatchTable1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2Table of monitored files. logMatchEntry1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1Entry of file logMatchIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.1Index of logmatchlogMatchName1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.2logmatchinstance namelogMatchFilename1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.3filename to be logmatchedlogMatchRegEx1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.4regular expression logMatchGlobalCounter1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.5global count of matches logMatchGlobalCounter1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.5Description. logMatchCurrentCounter1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.7Regular expression match counter. This counter resets with each log file rotation. logMatchCurrentCounter1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.7Description. logMatchCounter1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.9Regular expression match counter. This counter resets with each read logMatchCounter1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.9Description. logMatchCycle1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.11time between updates (if not queried) in seconds logMatchErrorFlag1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.100error setting: is this line configured correctly? logMatchRegExCompilation1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.16.2.1.101message of regular expression precompilationTable
version:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100Object Description versionIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.1Index to mib(always0)versionTag1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.2CVS tag keyword versionDate1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.3Date string from RCS keyword versionCDate1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.4Date string from ctime()versionIdent1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.5Id string from RCS keyword versionConfigureOptions1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.6Options passed to the configure script when this agent is built. versionClearCache1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.10Set to 1to clear theexeccache, if enabledversionUpdateConfig1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.11Set to 1to read-read the config file(s).versionRestartAgent1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.12Set to 1to restart the agent.versionSavePersistentData1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.13Set to 1to force the agent to save it's persistent data immediately.versionDoDebugging1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.20Set to 1to turn debugging statements on in the agent or0to turn off.Table
snmperrs:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.101Object Description snmperrIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.101.1Bogus Index for snmperrs(always0).snmperrNames1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.101.2snmp snmperrErrorFlag1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.101.100A Error setting to indicate trouble with the agent. Goes to 1if there is an error,0if no error.snmperrErrMessage1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.101.101An error message describing the problem (if one exists). Table
mrTable:1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.102Object Description mrEntry1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.102.1An entry containing a registered miboid.mrIndex1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.102.1.1The registry slot of a mibmodule.mrModuleName1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.102.1.2The module name that registered this OID.
IF-MIB
Table
ifTable:1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2Object Description ifEntry1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1An entry containing management information applicable to a particular interface. ifIndex1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1A unique value, greater than zero, for each interface. It is recommended that values are assigned contiguously starting from 1. The value for each interface sub-layer must remain constant at least from one re-initialization of the entity's network management system to the next re- initialization.ifDescr1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2A textual string containing information about the interface. This string must include the name of the manufacturer, the product name and the version of the interface hardware/software. ifType1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.3The type of interface. Additional values for ifTypeare assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), through updating the syntax of theIANAifTypetextual convention.ifMtu1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.4The size of the largest packet which can be sent/received on the interface, specified in octets. For interfaces that are used for transmitting network datagrams, this is the size of the largest network datagram that can be sent on the interface. ifSpeed1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5An estimate of the interface's current bandwidth in bits per second. For interfaces which do not vary in bandwidth or for those where no accurate estimation can be made, this object must contain the nominal bandwidth. If the bandwidth of the interface is greater than the maximum value reportable by this object then this object must report its maximum value ( 4,294,967,295) andifHighSpeedmust be used to report the interface's speed. For a sub-layer which has no concept of bandwidth, this object must be zero.ifPhysAddress1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6The interface's address at its protocol sub-layer. For example, for an 802.xinterface, this object normally contains a MAC address. The interface's media-specific MIB must define the bit and byte ordering and the format of the value of this object. For interfaces which do not have such an address (e.g., a serial line), this object must contain an octet string of zero length.ifAdminStatus1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.7The target state of the interface. The testing(3)state indicates that no operational packets can be passed. When a managed system initializes, all interfaces start withifAdminStatusin thedown(2)state. As a result of either explicit management action or per configuration information retained by the managed system,ifAdminStatusis then changed to either theup(1)ortesting(3)states (or remains in thedown(2)state).ifOperStatus1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8The current operational state of the interface. The testing(3) state indicates that no operational packets can be passed. If ifAdminStatusis down(2) thenifOperStatusmust bedown(2). IfifAdminStatusis changed toup(1)thenifOperStatusmust change toup(1)if the interface is ready to transmit and receive network traffic; it must change todormant(5)if the interface is waiting for external actions (such as a serial line waiting for an incoming connection); it must remain in thedown(2)state if and only if there is a fault that prevents it from going to theup(1)state; it must remain in thenotPresent(6)state if the interface has missing (typically, hardware) components.ifLastChange1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.9The value of sysUpTimeat the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state is entered prior to the last re-initialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value.ifInOctets1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10The total number of octets received on the interface, including framing characters. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifInUcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.11The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher (sub-)layer, which are not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sub-layer. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifInNUcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.12The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher (sub-)layer, which are addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sub-layer. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime. This object is deprecated in favour ofifInMulticastPktsandifInBroadcastPkts.ifInDiscards1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.13The number of inbound packets which are chosen to be discarded even though no errors are detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifInErrors1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.14For packet-oriented interfaces, the number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. For character- oriented or fixed-length interfaces, the number of inbound transmission units that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifInUnknownProtos1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.15For packet-oriented interfaces, the number of packets received via the interface which are discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol. For character-oriented or fixed-length interfaces that support protocol multiplexing the number of transmission units received via the interface which are discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol. For any interface that does not support protocol multiplexing, this counter always is 0. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifOutOctets1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.16The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing characters. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifOutUcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.17The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which are not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sub-layer, including those that are discarded or not sent. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifOutNUcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.18The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which are addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sub-layer, including those that are discarded or not sent. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime. This object is deprecated in favour ofifOutMulticastPktsandifOutBroadcastPkts.ifOutDiscards1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.19The number of outbound packets which are chosen to be discarded even though no errors are detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifOutErrors1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.20For packet-oriented interfaces, the number of outbound packets that are not transmitted because of errors. For character-oriented or fixed-length interfaces, the number of outbound transmission units that are not transmitted because of errors. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifOutQLen1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.21The length of the output packet queue (in packets). ifSpecific1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.22A reference to MIB definitions specific to the particular media being used to realize the interface. It is recommended that this value point to an instance of a MIB object in the media-specific MIB, i.e., that this object have the semantics associated with the InstancePointer textual convention defined in RFC 2579. In fact, it is recommended that the media-specific MIB specify what valueifSpecificmust/can take for values ofifType. If no MIB definitions specific to the particular media are available, the value must be set to the OBJECT IDENTIFIER {00}.Table
ifMIB:1.3.6.1.2.1.31Object Description ifMIBObjects1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1This data type is used to model an administratively assigned name of the owner of a resource. This information is taken from the NVT ASCII character set. It is suggested that this name contain one or more of the following: ASCII form of the manager station's transport address, management station name (e.g., domain name), network management personnel's name, location, or phone number. In some cases the agent itself is the owner of an entry. In these cases, this string shall be set to a string starting with agent.ifXTable1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1A list of interface entries. The number of entries is given by the value of ifNumber. This table contains additional objects for the interface table.ifXEntry1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1An entry containing additional management information applicable to a particular interface. ifName1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1The textual name of the interface. The value of this object must be the name of the interface as assigned by the local device and must be suitable for use in commands entered at the device's console. This might be a text name, such asle0or a simple port number, such as1, depending on the interface naming syntax of the device. If several entries in theifTabletogether represent a single interface as named by the device, then each has the same value ofifName. Note that for an agent which responds to SNMP queries concerning an interface on some other (proxied) device, then the value ofifNamefor such an interface is the proxied device's local name for it. If there is no local name, or this object is otherwise not applicable, then this object contains a zero-length string.ifInMulticastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.2The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher (sub-)layer, which are addressed to a multicast address at this sub-layer. For a MAC layer protocol, this includes both Group and Functional addresses. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifInBroadcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.3The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher (sub-)layer, which are addressed to a broadcast address at this sub-layer. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifOutMulticastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.4The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which are addressed to a multicast address at this sub-layer, including those that are discarded or not sent. For a MAC layer protocol, this includes both Group and Functional addresses. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifOutBroadcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.5The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which are addressed to a broadcast address at this sub-layer, including those that are discarded or not sent. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value of ifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCInOctets1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.6The total number of octets received on the interface, including framing characters. This object is a 64-bit version ofifInOctets. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCInUcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.7The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher (sub-)layer, which are not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sub-layer. This object is a 64-bit version ofifInUcastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCInMulticastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.8The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher (sub-)layer, which are addressed to a multicast address at this sub-layer. For a MAC layer protocol, this includes both Group and Functional addresses. This object is a 64-bit version ofifInMulticastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCInBroadcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.9The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a higher (sub-)layer, which are addressed to a broadcast address at this sub-layer. This object is a 64-bit version ofifInBroadcastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCOutOctets1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.10The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing characters. This object is a 64-bit version ofifOutOctets. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCOutUcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.11The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which are not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sub-layer, including those that are discarded or not sent. This object is a 64-bit version ofifOutUcastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCOutMulticastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.12The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which are addressed to a multicast address at this sub-layer, including those that are discarded or not sent. For a MAC layer protocol, this includes both Group and Functional addresses. This object is a 64-bit version ofifOutMulticastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifHCOutBroadcastPkts1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.13The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which are addressed to a broadcast address at this sub-layer, including those that are discarded or not sent. This object is a 64-bit version ofifOutBroadcastPkts. Discontinuities in the value of this counter can occur at re-initialization of the management system, and at other times as indicated by the value ofifCounterDiscontinuityTime.ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.14Indicates whether linkUp/linkDowntraps must be generated for this interface. By default, this object must have the value enabled(1) for interfaces which do not operate ontopof any other interface (as defined in theifStackTable), anddisabled(2)otherwise.ifHighSpeed1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.15An estimate of the interface's current bandwidth in units of 1,000,000bits per second. If this object reports a value ofnthen the speed of the interface is somewhere in the range ofn-500,000ton+499,999. For interfaces which do not vary in bandwidth or for those where no accurate estimation can be made, this object must contain the nominal bandwidth. For a sub-layer which has no concept of bandwidth, this object must be zero.ifPromiscuousMode1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.16This object has a value of false(2)if this interface only accepts packets/frames that are addressed to this station. This object has a value oftrue(1)when the station accepts all packets/frames transmitted on the media. The valuetrue(1)is only legal on certain types of media. If legal, setting this object to a value oftrue(1)requires the interface to be reset before becoming effective. The value ofifPromiscuousModedoes not affect the reception of broadcast and multicast packets/frames by the interface.ifConnectorPresent1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.17This object has the value true(1)if the interface sub-layer has a physical connector and the valuefalse(2)otherwise.ifAlias1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.18This object is an aliasname for the interface as specified by a network manager, and provides a non-volatilehandlefor the interface. On the first instantiation of an interface, the value ofifAliasassociated with that interface is the zero-length string. As and when a value is written into an instance ofifAliasthrough a network management set operation, then the agent must retain the supplied value in theifAliasinstance associated with the same interface for as long as that interface remains instantiated, including across all re-initializations/reboots of the network management system, including those which result in a change of the interface'sifIndexvalue. An example of the value which a network manager might store in this object for a WAN interface is the (Telco's) circuit number/identifier of the interface. Some agents support write-access only for interfaces having particular values ofifType. An agent which supports write access to this object is required to keep the value in non-volatile storage, but it limits the length of new values depending on how much storage is already occupied by the current values for other interfaces.ifCounterDiscontinuityTime1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.19The value of sysUpTimeon the most recent occasion at which any one or more of this interface's counters suffered a discontinuity. The relevant counters are the specific instances associated with this interface of anyCounter32orCounter64object contained in theifTableorifXTable. If no such discontinuities have occurred since the last re- initialization of the local management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value.ifStackTable1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.2The table containing information on the relationships between the multiple sub-layers of network interfaces. In particular, it contains information on which sub-layers run 'on top of' which other sub-layers, where each sub-layer corresponds to a conceptual row in the ifTable. For example, when the sub-layer withifIndexvalue x runs over the sub-layer withifIndexvalue y, then this table contains:ifStackStatus.x.y=activeFor eachifIndexvalue, I, which identifies an active interface, there are always at least two instantiated rows in this table associated with I. For one of these rows, I is the value ofifStackHigherLayer; for the other, I is the value ofifStackLowerLayer. (If I is not involved in multiplexing, then these are the only two rows associated with I.) For example, two rows exist even for an interface which has no others stacked on top or below it:ifStackStatus.0.x=active ifStackStatus.x.0=activeifStackEntry1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.2.1Information on a particular relationship between two sub-layers, specifying that one sub-layer runs on topof the other sub-layer. Each sub-layer corresponds to a conceptual row in theifTable.ifStackHigherLayer1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.2.1.1The value of ifIndexcorresponding to the higher sub-layer of the relationship, i.e., the sub-layer which runs ontopof the sub-layer identified by the corresponding instance ofifStackLowerLayer. If there is no higher sub-layer (below the internetwork layer), then this object has the value0.ifStackLowerLayer1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.2.1.2The value of ifIndexcorresponding to the lower sub-layer of the relationship, i.e., the sub-layer which runsbelowthe sub-layer identified by the corresponding instance ofifStackHigherLayer. If there is no lower sub-layer, then this object has the value0.ifStackStatus1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.2.1.3The status of the relationship between two sub-layers. Changing the value of this object from activetonotInServiceordestroyhas consequences up and down the interface stack. Thus, write access to this object is likely to be inappropriate for some types of interfaces, and many implementations choose not to support write-access for any type of interface.ifTestTable1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3This table contains one entry per interface. It defines objects which allow a network manager to instruct an agent to test an interface for various faults. Tests for an interface are defined in the media-specific MIB for that interface. After invoking a test, the object ifTestResultcan be read to determine the outcome. If an agent can not perform the test,ifTestResultis set to indicate. The objectifTestCodecan be used to provide further test-specific or interface-specific (or even enterprise-specific) information concerning the outcome of the test. Only one test can be in progress on each interface at any one time. If one test is in progress when another test is invoked, the second test is rejected. Some agents reject a test when a prior test is active on another interface.ifTestEntry1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3.1An entry containing objects for invoking tests on an interface. ifTestId1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3.1.1This object identifies the current invocation of the interface's test. ifTestStatus1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3.1.2This object indicates whether or not some manager currently has the necessary ownershiprequired to invoke a test on this interface. A write to this object is only successful when it changes its value fromnotInUse(1)toinUse(2). After completion of a test, the agent resets the value back tonotInUse(1).ifTestType1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3.1.3A control variable used to start and stop operator- initiated interface tests. Most OBJECT IDENTIFIER values assigned to tests are defined elsewhere, in association with specific types of interface. However, this document assigns a value for a full-duplex loopback test, and defines the special meanings of the subject identifier: noTest OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { 0 0 }When the valuenoTestis written to this object, no action is taken unless a test is in progress, in which case the test is aborted. Writing any other value to this object is only valid when no test is currently in progress, in which case the indicated test is initiated. When read, this object always returns the most recent value thatifTestTypeis set to. If it has not been set since the last initialization of the network management subsystem on the agent, a value ofnoTestis returned.ifTestResult1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3.1.4This object contains the result of the most recently requested test, or the value none(1)if no tests have been requested since the last reset. Note that this facility provides no provision for saving the results of one test when starting another, as required if used by multiple managers concurrently.ifTestCode1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3.1.5This object contains a code which contains more specific information on the test result, for example an error-code after a failed test. Error codes and other values this object takes are specific to the type of interface and test. The value has the semantics of either the AutonomousTypeorInstancePointertextual conventions as defined in RFC2579. The identifier:testCodeUnknown OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { 0 0 }is defined for use if no additional result code is available.ifTestOwner1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.3.1.6The entity which currently has the ownershiprequired to invoke a test on this interface.ifRcvAddressTable1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.4This table contains an entry for each address (broadcast, multicast, or unicast) for which the system receives packets/frames on a particular interface, except as follows: - for an interface operating in promiscuous mode, entries are only required for those addresses for which the system receives frames are it not operating in promiscuous mode. - for 802.5functional addresses, only one entry is required, for the address which has the functional address bitANDedwith the bit mask of all functional addresses for which the interface accepts frames. A system is normally able to use any unicast address which corresponds to an entry in this table as a source address.ifRcvAddressEntry1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.4.1A list of objects identifying an address for which the system accept packets/frames on the particular interface identified by the index value ifIndex.ifRcvAddressAddress1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.4.1.1An address for which the system accepts packets/frames on this entry's interface. ifRcvAddressStatus1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.4.1.2This object is used to create and delete rows in the ifRcvAddressTable.ifRcvAddressType1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.4.1.3This object has the value nonVolatile(3)for those entries in the table which are valid and are not deleted by the next restart of the managed system. Entries having the valuevolatile(2)are valid and exist, but have not been saved, that does not exist after the next restart of the managed system. Entries having the valueother(1)are valid and exist but are not classified as to whether they continue to exist after the next restart.ifTableLastChange1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.5The value of sysUpTimeat the time of the last creation or deletion of an entry in theifTable. If the number of entries has been unchanged since the last re-initialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value.ifStackLastChange1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.6The value of sysUpTimeat the time of the last change of the (whole) interface stack. A change of the interface stack is defined to be any creation, deletion, or change in value of any instance ofifStackStatus. If the interface stack has been unchanged since the last re-initialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value.ifConformance1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2The compliance statement for SNMP entities which have network interfaces. ifGroups1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1The compliance statement for SNMP entities which have network interfaces. ifGeneralGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.1A collection of objects deprecated in favour of ifGeneralInformationGroup.ifFixedLengthGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.2A collection of objects providing information specific to non-high speed (non-high speed interfaces transmit and receive at speeds less than or equal to 20,000,000bits/second) character-oriented or fixed-length-transmission network interfaces.ifHCFixedLengthGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.3A collection of objects providing information specific to high speed (greater than 20,000,000bits/second) character- oriented or fixed-length-transmission network interfaces.ifPacketGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.4A collection of objects providing information specific to non-high speed (non-high speed interfaces transmit and receive at speeds less than or equal to 20,000,000bits/second) packet-oriented network interfaces.ifHCPacketGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.5A collection of objects providing information specific to high speed (greater than 20,000,000bits/second but less than or equal to650,000,000bits/second) packet-oriented network interfaces.ifVHCPacketGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.6A collection of objects providing information specific to higher speed (greater than 650,000,000bits/second) packet- oriented network interfaces.ifRcvAddressGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.7A collection of objects providing information on the multiple addresses which an interface receives. ifTestGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.8A collection of objects providing the ability to invoke tests on an interface. ifStackGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.9The previous collection of objects providing information on the layering of MIB-II interfaces. ifGeneralInformationGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.10A collection of objects providing information applicable to all network interfaces. ifStackGroup21.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.11A collection of objects providing information on the layering of MIB-II interfaces. ifOldObjectsGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.12The collection of objects deprecated from the original MIB- II interfaces group. ifCounterDiscontinuityGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.13A collection of objects providing information specific to interface counter discontinuities. linkUpDownNotificationsGroup1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.1.14The notifications which indicate specific changes in the value of ifOperStatus.ifCompliances1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.2The compliance statement for SNMP entities which have network interfaces. ifCompliances1.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.2A compliance statement defined in a previous version of this MIB module, for SNMP entities which have network interfaces. ifCompliance21.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.2.2A compliance statement defined in a previous version of this MIB module, for SNMP entities which have network interfaces. ifCompliance31.3.6.1.2.1.31.2.2.3The compliance statement for SNMP entities which have network interfaces.