Formatting Functions
Overview
These functions format numbers, dates, collections, and maps to strings according to the specified format.
Reference
Number formatting functions:
Number formatting objects:
Related date formatting functions and objects:
formatNumber
formatNumber(number x, string pattern) string
Formats number x with the specified DecimalFormat pattern using the server locale (US/US).
Example:
// returns 3.14
formatNumber(3.14159, '#.##')
1234.5678 #.## -> 1234.56
1234.5678 #.### -> 1234.567
1234.5678 #,###.### -> 1,234.567
0.5678 #.## -> .56
0.5678 0.## -> 0.56
10 #.# -> 10
10 #.0 -> 10.0
NumberFormatter
NumberFormatter(string pattern [, string locale])
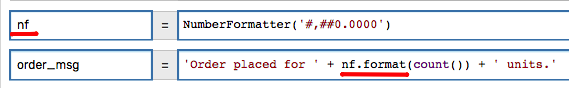
Unlike functions, which convert an input number to a string, the NumberFormatter is an object which is configured once as a variable and re-used to format any number into string using the same pattern and locale.
The formatter object provides two methods: format() and print() which return the same result.
Example:
// formatter is initialized as variable
nf = NumberFormatter('0.00')
// formatter is used to format numbers
nf.format(10) -> 10.00
nf.format(3.1415) -> 3.14
// format and add backticks for markdown
nf = NumberFormatter('`#,##0.0`')
formatPrecision
formatPrecision(double x, int digits) string
Formats number x based on toPrecision rules.
The digits must be between 1 and 100.
Example:
formatPrecision(3.14159265, 3) // 3.14
formatPrecision(3.14159265, 4) // 3.142
formatPrecision(10, 4) // 10.00
formatBytes
formatBytes(number x, bool si) string
Returns the total number of bytes x in human-readable format. Identifies the largest possible unit (from Byte to Exabyte) such that the number x is equal to or exceeds 1 such unit. Units are decimal-based (1000) if the si parameter is set to true, and binary (1024) otherwise.
For example, if the unit is 1000 (si set to true):
999 -> 999.0 B (unit is byte)
1000 -> 1.0 kB (unit is kilobyte)
Formatted number always contains one fractional digit.
Examples:
si=false si=true
0: 0 B 0 B
27: 27 B 27 B
999: 999 B 999 B
1000: 1.0 kB 1000 B
1023: 1.0 kB 1023 B
1024: 1.0 kB 1.0 KiB
1728: 1.7 kB 1.7 KiB
110592: 110.6 kB 108.0 KiB
7077888: 7.1 MB 6.8 MiB
452984832: 453.0 MB 432.0 MiB
28991029248: 29.0 GB 27.0 GiB
1855425871872: 1.9 TB 1.7 TiB
Unexpected Inputs
If the x argument is a string or an object that cannot be parsed into a number, the function returns the original value x.
convert
convert(number x, string unit) string
Divides the number x by the specified measurement unit and formats the returned string with one fractional digit.
The unit is case-insensitive and can be one of the following:
K,Kb(1000)Ki,KiB(1024)M,Mb(1000^2)Mi,MiB(1024^2)G,Gb(1000^3)Gi,GiB(1024^3)T,Tb(1000^4)Ti,TiB(1024^4)P,Pb(1000^5)Pi,PiB(1024^5)E,Eb(1000^6)Ei,EiB(1024^6)
Examples:
// Returns 20.0
// same as formatNumber(20480/1024, '#.#')
convert(20480, 'KiB') // 20.0
convert(1000 * 1000, 'M') // 1.0
