Window
Overview
A window is an in-memory structure created by the rule engine for each unique combination of metric, entity, and grouping tags extracted from incoming commands.
Windows are displayed on the Alerts > Rule Windows page and provide access to fields.
Count-based Windows
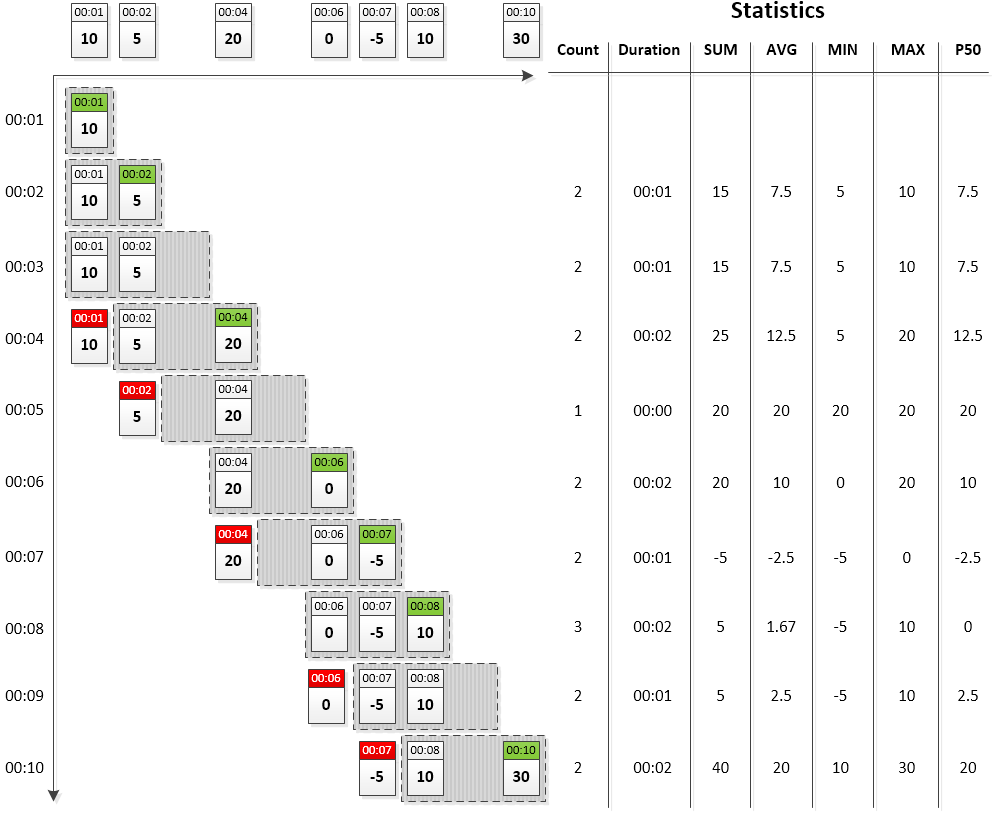
Count-based windows accumulate up to the specified number of time-value samples. Samples are sorted by command timestamp, with the most recent sample placed at the end of the array. When the window becomes full, the first sample (oldest by command time) is removed from the window to free up space for an incoming sample.
Example: Count-based window with three samples.
Once the above window reaches the limit of three samples, its size remains constant.
Time-based Windows
Time-based windows store all samples received within the specified time interval and are referred to as sliding windows. There is no limit to the number of samples stored in such windows.
Old commands are automatically removed from the window once their timestamp is earlier than the window start time.
Example: 5-second window with variable sample count.
The number of samples is not limited and varies over time from one to four. Such windows can become empty if no commands arrive within a certain period of time.
Window Boundaries
The start time of the time-based window is initially set to current time minus the interval duration, and is constantly incremented as time passes. If the timestamp of the incoming command is equal to or greater than the window start time, the command is added to the window. Otherwise, the command is ignored.
The end time in time-based windows is not bound. As such, the window accepts commands with future timestamps unless they are discarded with the Time Offset filter or filter expression such as timestamp < now.millis + 60000.
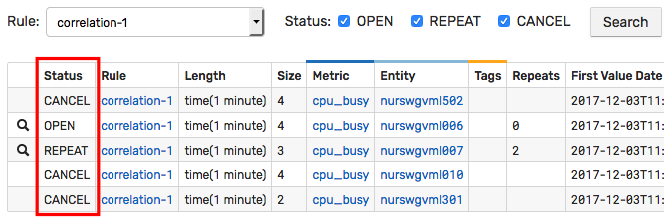
Window Status
Response actions are triggered on window status changes.
As new commands are received and expired commands are removed from the window, the rule engine re-evaluates the condition which can cause the status of the current window to change, triggering response actions.
Initial Status
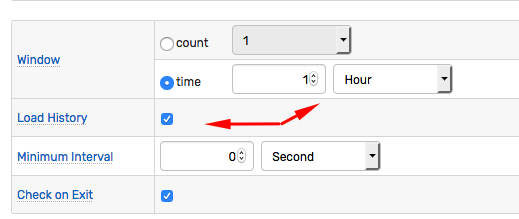
New windows are created from incoming commands. No historical data is loaded from the database unless the Load History setting is turned on.
The window for the given grouping key is created when the first matching command is received by the rule engine.
New windows are assigned initial status of CANCEL which is then updated based on the results of a boolean condition, either true or false.
Triggers
Response actions can be triggered whenever window status changes as well as at scheduled intervals when the status is REPEAT. Triggers for each action are configured and executed separately.
Status Events
| Previous Status | New Status | Previous Condition Value | New Condition Value | Trigger Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
CANCEL | OPEN | false | true | On Open |
OPEN | REPEAT | true | true | On Repeat |
REPEAT | REPEAT | true | true | On Repeat |
OPEN | CANCEL | true | false | On Cancel |
REPEAT | CANCEL | true | false | On Cancel |
CANCEL | CANCEL | false | false | Not available |
OPEN Status
The window is assigned OPEN status when the condition value changes from false to true.
REPEAT Status
The window is assigned REPEAT status when the condition value remains true upon subsequent evaluation. REPEAT status requires at least two true consecutive evaluations.
When the window is in REPEAT status, response actions can be executed with the frequency specified in the rule editor, for example, every ten evaluations or every five minutes.
CANCEL Status
CANCEL is the initial status assigned to new windows. The CANCEL status is also assigned to the window when the condition changes from true to false or when the window is destroyed on rule modification.
Windows in CANCEL status do not trigger repeat actions upon subsequent false evaluations. Emulate this behavior by creating a rule with a negated expression which returns true instead of false for the same condition.
A window assumes the CANCEL status when the condition changes from true to false as well as when the rule is modified, deleted, or the database is orderly shutdown. On Cancel triggers are not invoked, even if enabled, when the rule is modified, deleted, or in case of shutdown. This behavior is controlled with cancel.on.rule.change server property.
Life Cycle
When a rule is saved after changing the filters, grouping fields or the condition, all windows for the given rule are removed. Changes in notifications do no affect current windows.
Windows are re-created when new matching commands are received by the database.
Newly created windows contain only new commands, unless Load History setting is enabled. Such windows load historical values received over the same interval as the window duration, or the same number of commands as the window length.
Timers
The condition is re-evaluated each time a new matching command is added to or removed from the window.
To evaluate the rule on schedule, regardless of external commands, create rules based on timer metrics:
timer_15s: Command is received every 15 seconds.timer_1m: Command is received every 1 minute.timer_15m: Command is received every 15 minutes.timer_1h: Command is received every 1 hour.
timer metrics are produced by the built-in database scheduler and are always available.
Window Fields
Windows expose a set of continuously updated window fields which can be included in the condition expression, the filter expression and user-defined variables.
Window Diagrams
Count-based Window Diagram
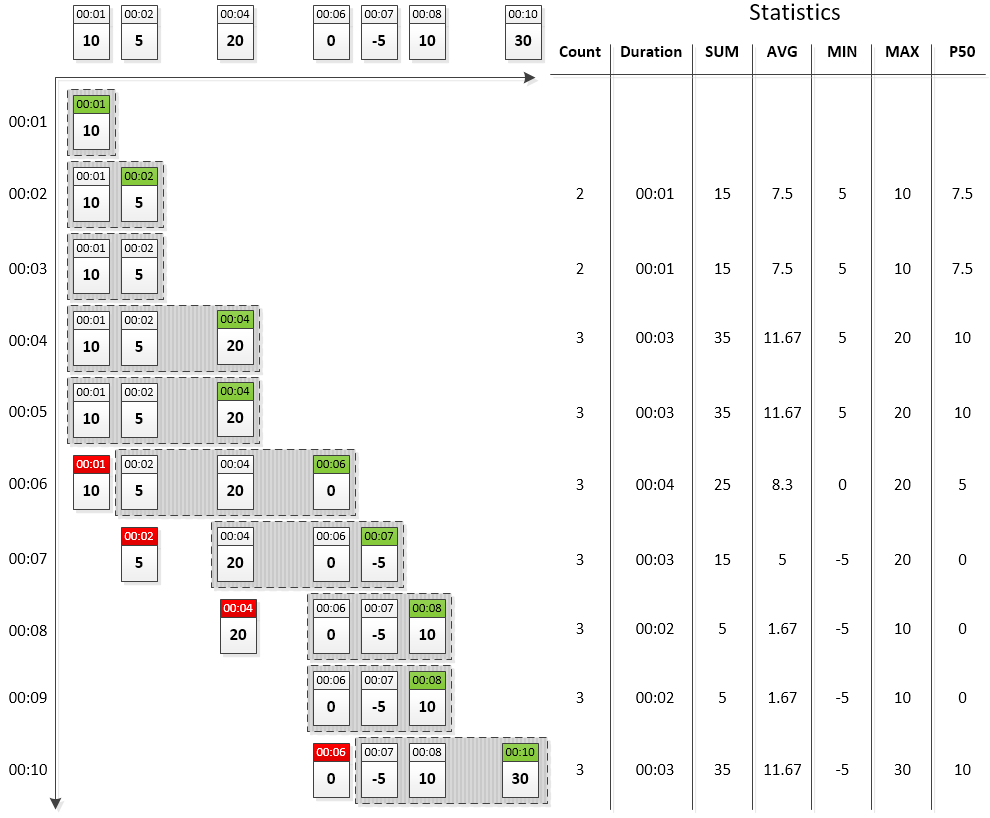
Time-based Window Diagram