Format Settings
Reference
Basic Formats
The format setting supports the following functions.
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
decimal | Formats a number up to the specified number of fractional digits. Example: format = decimal(2) // 3.10 > 3.1 | ↗ |
fixed | Formats a number to the fixed number of fractional digits. The input value is not rounded. Example: format = fixed(2) // 1.5 > 1.50 | ↗ |
precise | Formats a number to a specific precision. Refer to Number.prototype.toPrecision().Example: format = precise(3) // 0.5 > 0.500 | ↗ |
currency | Currency formatting. Indicate units as an argument in the currency expression.Decimal values rounded to 1 fractional digit.Example: format = '$' + currency('million') // 6.3 > $6.3M. | ↗ |
By default the functions are applied to the sample value at each timestamp.
Arguments
The decimal, fixed, and precise functions accept an optional value argument which can be an arithmetic expression.
fixed([number value, ] integer digits)
Examples
fixed(value, 3); // 3.14159 -> 3.141
fixed(3); // 3.14159 -> 3.141
fixed(2); // 3.14159 -> 3.14
fixed(1); // 3.14159 -> 3.1
fixed(0); // 3.14159 -> 3
fixed(0); // 12345.6 -> 12345
fixed(3.14159, 3); // 3.14159 -> 3.141
fixed(value*2, 3); // 3.14159 -> 6.2
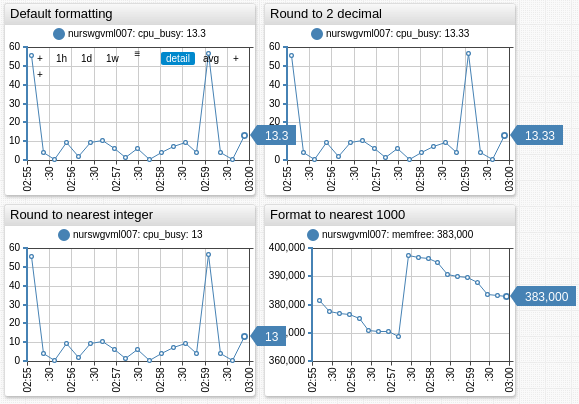
Rounding
round([number value, ] integer digits)
Rounds the input value.
- if
digits > 0, thevalueis rounded to the specified number of decimal places; - if
digits = 0, thevalueis rounded to the nearest integer; - if
digits < 0, thevalueis rounded to the left of the decimal point.
The value to be formatted is optional and can be specified as an arithmetic expression. By the default the input value is set to value of the sample at the given timestamp.
Examples
format = round(0)
format = round(value/512, 1)
format = round(-3)
| Operation | Syntax |
|---|---|
12.34 rounded to 12.3 | format = round(1) |
12.34 rounded to 12 | format = round(0) |
12.34 rounded to 10 | format = round(-1) |
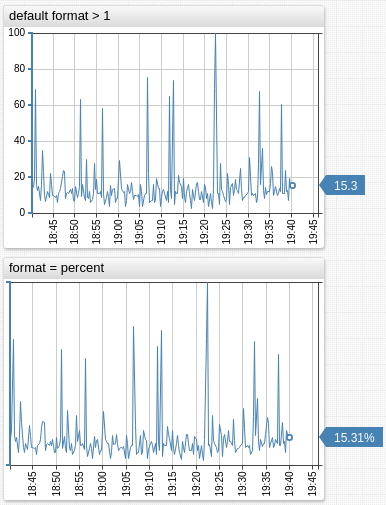
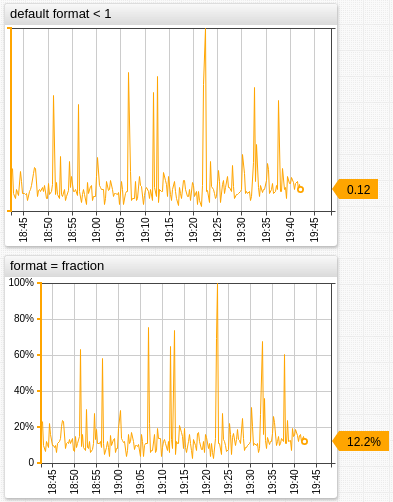
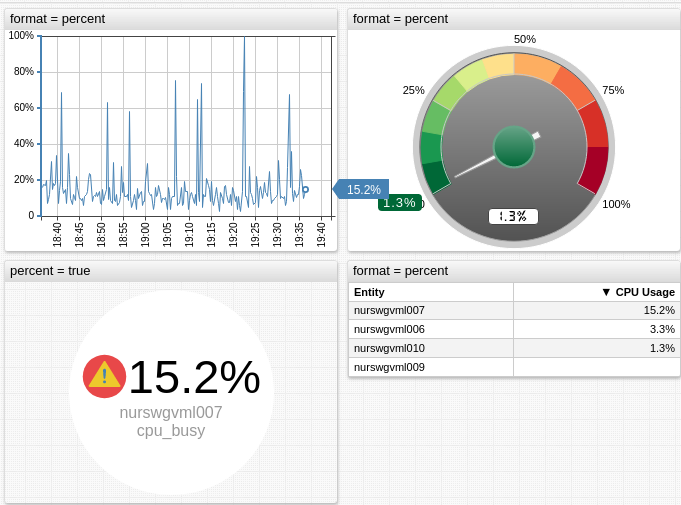
Percentages
percent([integer digits])
fraction([integer digits])
Formats the input value as a percentage of 100. The number of decimal places is controlled with digits, default is 0.
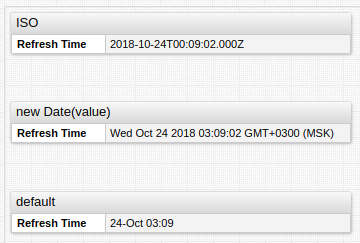
Dates
| Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
format = iso | ISO format. |
format = new Date(value) | Print time in current locale. |
format = (new Date(value)).toISOString | Print current locale time in ISO format. |
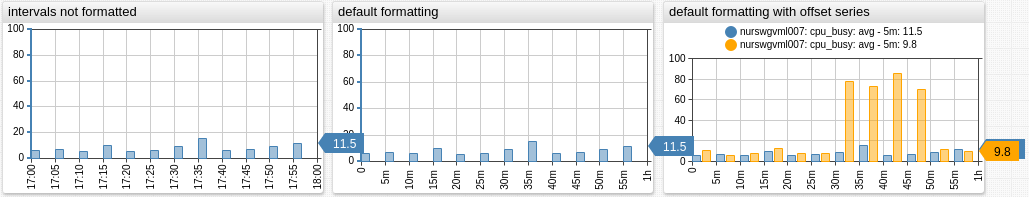
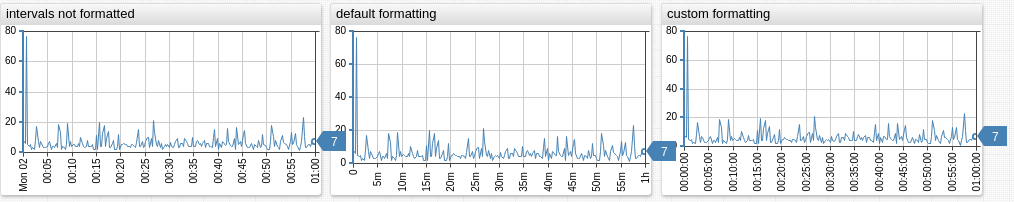
Intervals
Format series values with millisecond timestamps using the intervalFormat function or the interval-format setting.
/* call intervalFormat function */
format = intervalFormat('%dd %H:%M:%S')(value*1000)
/* apply the default format */
interval-format = true
/* apply custom format */
interval-format = %H:%M
2019-04-05T16:01:33Z - %H:%M:%S - 16:01:33
2019-04-05T16:01:33Z - %H:%M - 16:01
Supported Placeholders
%d: Day%Hand%h: Hour%Mand%m: Minute%Sand%s: Second%Land%l: Millisecond
Examples
Day Format
The date format controls how time is displayed on the X-axis as well as in sample tooltips.
The date format consists of two settings: day-format and hour-format.
The day-format setting controls the date part of the labels displayed on the time axis.
Syntax
Common patterns:
%d: Zero-padded day of the month[01,31].%m: Month number[01,12].%b: Abbreviated month name.%y: Year without century[00,99].%Y: Year with century.%a: Three-letter abbreviated day name:Sun,Mon,Tue,Wed,Thu,Fri,Sat.
Additional patterns:
%aa: Two-letter abbreviated day name:Su,Mo,Tu,We,Th,Fr,Sa.%A: Full day name.%B: Full month name.%e: Space-padded day of the month as a decimal number[ 1,31]. Equivalent to%_d.%j: Day of the year as a decimal number[001,366].%U: Week number of the year as a decimal number[00,53]. Sunday is the first day of the week.%w: Weekday as a decimal number[0(Sunday),6].%W: Week number of the year as a decimal number[00,53]. Monday is the first day of the week.
The pattern can include other characters, for example line break \n to conserve horizontal space by placing date units on separate lines.
Related setting to control the number of ticks on the time axis:
ticks-time.
Examples
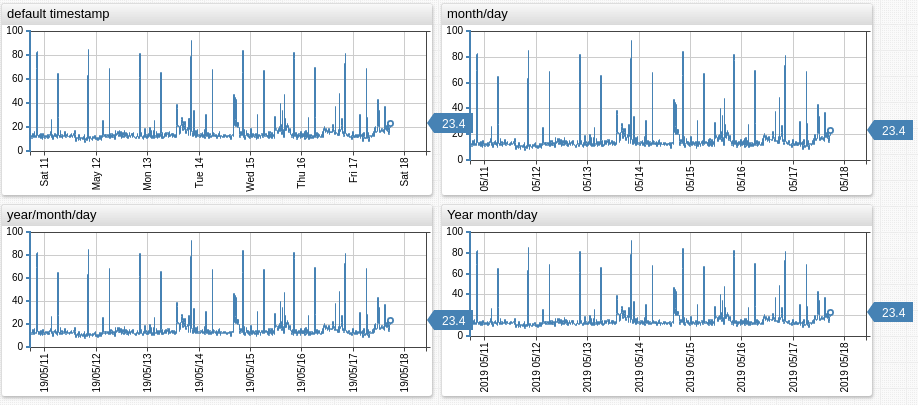
- Input date is 2019-03-11 (Monday).
day-format = %m/%d # -> 03/11
day-format = %y/%m/%d # -> 19/03/11
day-format = %Y/%m/%d # -> 2019/03/11
day-format = %b-%d # -> Mar-11
day-format = %d\n%aa # -> 11 Mo (placed on separate lines)
Hour Format
Control the time format for the X-axis for hour and minute.
Syntax
Use any combination of the following:
%H: 24-hour time hour as a decimal number[00,23].%I: 12-hour time hour as a decimal number[01,12].%M: Minute as a decimal number[00,59].%p: AM or PM.%X: time, as%H:%M:%S.
Line break syntax
/nis supported.
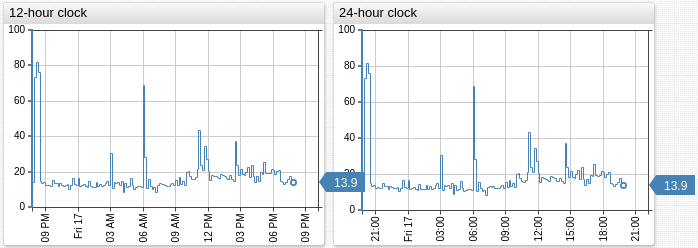
Examples
hour-format = %I %p
hour-format = %H:%M
Measurement Units
format = bytes
format = kilobytes
format = megawatt
format = kilowatthour
format = hertz
format = kilojoule
format = million watt
format = thousands
JSON
format = json
Formats the text as a JSON document and applies syntax highlighting.